Foaming and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Pastes Manufactured from Post-Metallurgical Recycled Slag
- PMID: 38541603
- PMCID: PMC10971870
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17061449
Foaming and Physico-Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Pastes Manufactured from Post-Metallurgical Recycled Slag
Abstract
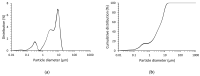
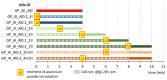
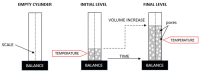
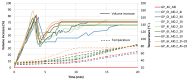
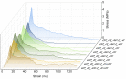
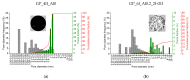
This paper presents a research program aimed towards developing a method of producing lightweight, porous geopolymer composites for the construction industry based on industrial wastes. A direct method involving the addition of chemicals is currently most commonly used to produce the porous mineral structure of a geopolymer matrix. This relies on a reaction in a highly alkaline environment of the geopolymer to produce a gas (usually hydrogen or oxygen) that forms vesicles and creates a network of pores. This paper demonstrates the feasibility of producing a slag-based geopolymer paste foamed with aluminum powder, taking into account different parameters of fresh paste production: the mixing duration, its speed and the timing of foaming agent addition. The foaming process of the fresh paste in terms of the volumetric changes and temperature development of the fresh paste during the curing of the material are observed. After hardening, the physical properties (density and porosity) as well as the mechanical parameters (compressive strength and work of damage) are determined for the nine manufactured foamed pastes. Image analysis software was used to assess the porosity distribution of the material across the cross-section of the samples. The results enabled the design of the mixing procedure to be adopted during the manufacture of such composites.
Keywords: foamed geopolymer; industry waste; paste; pore size distribution; porous materials; stereology; work of damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chen Z., Yu J., Nong Y., Yang Y., Zhang H., Tang Y. Beyond Time: Enhancing Corrosion Resistance of Geopolymer Concrete and BFRP Bars in Seawater. Compos. Struct. 2023;322:117439. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.117439. - DOI
-
- Zhong W.L., Sun Y.H., Zhao X., Fan L.F. Study on Synthesis and Water Stability of Geopolymer Pavement Base Material Using Waste Sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2024;445:141331. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141331. - DOI
-
- Guo T., Ma F., Shen P., Wang X., Bai X., An Y., Huang Z., Bai X., Han P. The Setting and Hardening of Geopolymer Concrete Based on Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Cyclic Voltammetry Methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024;418:135471. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135471. - DOI
-
- Pacheco-Torgal F., Abdollahnejad Z., Camões A.F., Jamshidi M., Ding Y. Durability of Alkali-Activated Binders: A Clear Advantage over Portland Cement or an Unproven Issue? Constr. Build. Mater. 2012;30:400–405. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.12.017. - DOI
-
- Turner L.K., Collins F.G. Carbon Dioxide Equivalent (CO2-e) Emissions: A Comparison between Geopolymer and OPC Cement Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013;43:125–130. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.01.023. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

