Neuropancreatology: The Nervous System and Pain Management in Pancreatic Diseases
- PMID: 38541624
- PMCID: PMC10970869
- DOI: 10.3390/life14030299
Neuropancreatology: The Nervous System and Pain Management in Pancreatic Diseases
Abstract
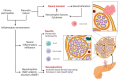
The intricate network of the pancreatic nervous system plays a fundamental role in physiologic functions of the endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Several pancreatic diseases affect the normal functionality of the pancreatic nervous system. This chronic derangement leads to anatomical alterations, such as neural hypertrophy and increased nerve density. Perineural invasion is a prominent feature of pancreatic cancer, contributing to cancer progression and metastasis. Despite the fact that these pathogenic mechanisms are still incompletely studied and understood, the constant occurrence of these alterations highlights their importance in the pathophysiology of the pancreatic diseases. The occurrence of anatomical changes is strictly linked to the appearance of pain. Pancreatic pain has peculiar features, and its management is complex in clinical practice. In the present review, the evidence on lifestyle, pharmacological and interventional approaches for the management of pancreatic pain is presented. Analgesic therapy is the cornerstone of pain treatment. However, it is important to identify the individual characteristic of the patients and personalize the approach to pain management. Nevertheless, the incomplete efficacy of these strategies makes this field an area of unmet needs. The study of neuroplasticity is crucial to understand the mechanisms that regulate the pathophysiology of pancreatic diseases. Several trials testing new drugs with specific neuromodulatory effects are ongoing. However, further studies are needed to investigate crucial targets to develop novel therapies for the modulation of the nervous system and the prevention of complications of pancreatic diseases. This comprehensive review summarizes the importance of the nervous system in pancreatic diseases with a special focus on its anatomy and physiology, its pathophysiological features and clinical relevance in pancreatic disease, the treatment of pancreatic pain, and the identification of future trends of research.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; chronic pancreatitis; neural plasticity; neuromodulation; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic nervous system; pancreatic pain; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural plasticity in pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov;12(11):649-59. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.166. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26460352 Review.
-
Evidence of pancreatic neuropathy and neuropathic pain in hereditary chronic pancreatitis.Pancreatology. 2013 Nov-Dec;13(6):629-30. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Pancreatology. 2013. PMID: 24280582
-
Pancreatic neuropathy and neuropathic pain--a comprehensive pathomorphological study of 546 cases.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jan;136(1):177-186.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.029. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 18992743
-
Tumor microenvironment crosstalk between tumors and the nervous system in pancreatic cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical perspectives.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Jan;1879(1):189032. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189032. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38036106 Review.
-
Pancreatic Morphology, Immunology, and the Pathogenesis of Acute Pancreatitis.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 17;12(11):2627. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12112627. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39595191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The supporting role of Schwann cells in perineural invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 11;16:1540027. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540027. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40567365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iannuzzi J.P., King J.A., Leong J.H., Quan J., Windsor J.W., Tanyingoh D., Coward S., Forbes N., Heitman S.J., Shaheen A.-A., et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:122–134. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD2017 Pancreatic Cancer Collaborators The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019;4:934–947. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30347-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

