A Comparative Study: Cardioprotective Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Ischaemic Preconditioning in Rat Myocardial Ischaemia-Reperfusion
- PMID: 38541636
- PMCID: PMC10971567
- DOI: 10.3390/life14030310
A Comparative Study: Cardioprotective Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Ischaemic Preconditioning in Rat Myocardial Ischaemia-Reperfusion
Abstract
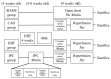
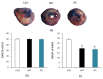
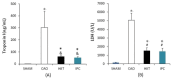
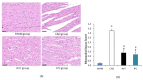
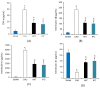
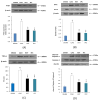
(1) Background: Years of research have identified ischemic preconditioning (IPC) as a crucial endogenous protective mechanism against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, enhancing the myocardial cell's tolerance to subsequent ischemic damage. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is promoted by athletes because it reduces exercise duration and improves metabolic response and cardiopulmonary function. Our objective was to evaluate and compare whether HIIT and IPC could reduce myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. (2) Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups: sham surgery, coronary artery occlusion (CAO), high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and ischemic preconditioning (IPC). The CAO, HIIT, and IPC groups experienced 40 min of coronary artery occlusion followed by 3 h of reperfusion to induce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Subsequently, the rats were sacrificed, and blood samples along with cardiac tissues were examined. The HIIT group received 4 weeks of training before surgery, and the IPC group underwent preconditioning before the ischemia-reperfusion procedure. (3) Results: The HIIT and IPC interventions significantly reduced the extent of the myocardial infarction size and the levels of serum troponin I and lactate dehydrogenase. Through these two interventions, serum pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, were significantly decreased, while the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was increased. Furthermore, the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins PTEN, caspase-3, TNF-α, and Bax in the myocardium was reduced, and the expression of anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) was increased, ultimately reducing cellular apoptosis in the myocardium. In conclusion, both HIIT and IPC demonstrated effective strategies with potential for mitigating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury for the heart.
Keywords: apoptosis; coronary artery occlusion; high-intensity interval training; ischemic preconditioning; myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-intensity interval training attenuates renal injury induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in rats.J Chin Med Assoc. 2025 Feb 1;88(2):126-137. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000001183. Epub 2024 Oct 22. J Chin Med Assoc. 2025. PMID: 39965790
-
High-intensity interval training increases myocardial levels of Klotho and protects the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury.Exp Physiol. 2020 Apr;105(4):652-665. doi: 10.1113/EP087994. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32052504
-
Ischaemic preconditioning-induced serum exosomes protect against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Mar;39(2):287-295. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3578. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 32767595
-
Protective effects of circulating microvesicles derived from ischemic preconditioning on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress.Apoptosis. 2018 Aug;23(7-8):436-448. doi: 10.1007/s10495-018-1469-4. Apoptosis. 2018. PMID: 29980896
-
Advances in organ protection: ischemic preconditioning and erythropoietin as protective strategies.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun 2. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04586-z. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40455321 Review.
Cited by
-
Tongxinluo capsule as a multi-functional traditional Chinese medicine in treating cardiovascular disease: A review of components, pharmacological mechanisms, and clinical applications.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 21;10(13):e33309. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33309. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-intensity interval training improves mitochondrial function and attenuates cardiomyocytes damage in ischemia-reperfusion.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025 Jul 25;60:101756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2025.101756. eCollection 2025 Oct. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025. PMID: 40756748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shao C., Wang J., Tian J., Tang Y.D. Coronary artery disease: From mechanism to clinical practice. Coron. Artery Dis. Ther. Drug Discov. 2020;1177:1–36. - PubMed
-
- Popgeorgiev N., Sa J.D., Jabbour L., Banjara S., Nguyen T.T.M., Akhavan-E-Sabet A., Gadet R., Ralchev N., Manon S., Hinds M.G., et al. Ancient and conserved functional interplay between Bcl-2 family proteins in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eabc4149. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc4149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

