Magnolol Reduces Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in BALB/c Mice
- PMID: 38541664
- PMCID: PMC10971286
- DOI: 10.3390/life14030339
Magnolol Reduces Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
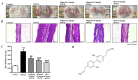
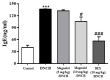
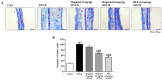
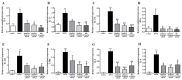
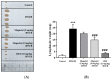
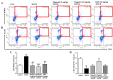
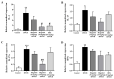
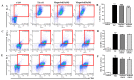
In traditional Korean medicines, Magnolia officinalis is commonly included for the remedy of atopic dermatitis, and magnolol is a major constituent of Magnolia officinalis. Its pharmacological effects include anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, and antioxidant effects. Using BALB/c mice repeatedly exposed to 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DNCB), magnolol was evaluated in atopic dermatitis-like lesions. Administration of magnolol (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) markedly relieved the skin lesion severity including cracking, edema, erythema, and excoriation, and significantly inhibited the increase in IgE levels in the peripheral blood. A DNCB-induced increase in mast cell accumulation in atopic dermatitis skin lesions was reversed by magnolol administration, as well as a rise in expression levels of pro-inflammatory Th2/Th17/Th1 cytokines' (IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IFN-γ, IL-12A, TARC, IL-8, and IL-6) mRNAs in the lymph nodes and skin (n = 5 per group). In lymph nodes, magnolol reversed DNCB's increase in CD4+RORγt+ Th17 cell fraction and decrease in CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cell fraction. The results also showed that magnolol suppressed T cell differentiation into Th17 and Th2 cells, but not Th1 cells. Magnolol suppresses atopic dermatitis-like responses in the lymph nodes and skin, suggesting that it may be feasible to use it as a treatment for atopic dermatitis through its suppression of Th2/Th17 differentiation.
Keywords: Magnolia officinalis; anti-atopy; atopic dermatitis; atopy; dermatitis; magnolia; magnolol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GPR55 antagonist CID16020046 suppresses DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms by suppressing Th1/Th2/Th17 populations in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 15;985:177088. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177088. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39486767
-
Honokiol suppresses 2,6-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 May 10;289:115023. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115023. Epub 2022 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35074454
-
Evodiamine Alleviates 2,4-Dinitro-1-Chloro-Benzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in BALB/c Mice.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;14(4):494. doi: 10.3390/life14040494. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672764 Free PMC article.
-
Blockage of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Nov;41(11):1487-1496. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0412-8. Epub 2020 May 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32457418 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cytokines/chemokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis.Curr Probl Dermatol. 2011;41:80-92. doi: 10.1159/000323299. Epub 2011 May 12. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21576949 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effects of Natural Products on Human Diseases.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;14(9):1166. doi: 10.3390/life14091166. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silverberg J.I., Barbarot S., Gadkari A., Simpson E.L., Weidinger S., Mina-Osorio P., Rossi A.B., Brignoli L., Saba G., Guillemin I. Atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population: A cross-sectional, international epidemiologic study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:417–428.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paller A.S., Simpson E.L., Siegfried E.C., Cork M.J., Wollenberg A., Arkwright P.D., Soong W., Gonzalez M.E., Schneider L.C., Sidbury R. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;400:908–919. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01539-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Graff P. Ph.D. Thesis. Freie University; Berlin, Germany: 2022. Potential Drivers of the Atopic March-Unraveling the Skin-Lung Crosstalk.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

