Circulating microRNAs in Cancer: A 5-Year Update with a Focus on Breast and Lung Cancers
- PMID: 38542114
- PMCID: PMC10969845
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063140
Circulating microRNAs in Cancer: A 5-Year Update with a Focus on Breast and Lung Cancers
Abstract
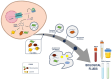
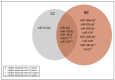
Circulating microRNAs (c-miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs found in different bodily fluids and are highly investigated for their prognostic potential and biological role in cancer. In this narrative review, we provide an update of the last five years' published papers (2018-2023) on PubMed about c-miRNAs in cancer research. We aim to capture the latest research interests in terms of the highly studied cancers and the insights about c-miRNAs. Our analysis revealed that more than 150 papers focusing on c-miRNAs and cancer were published in the last five years. Among these, there was a high prevalence of papers on breast cancer (BC) and lung cancer (LC), which are estimated to be the most diagnosed cancers globally. Thus, we focus on the main evidence and research trends about c-miRNAs in BC and LC. We report evidence of the effectiveness of c-miRNAs in hot topics of cancer research, such as, early detection, therapeutic resistance, recurrence risk and novel detection platform approaches. Moreover, we look at the deregulated c-miRNAs shared among BC and LC papers, focusing on miR-21 and miR-145. Overall, these data clearly indicate that the role of c-miRNAs in cancer is still a hot topic for oncologic research and that blood is the most investigated matrix.
Keywords: breast cancer; immunotherapy; lung cancer; miRNAs; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic Analysis Divulged Novel Prognostic Circulating MicroRNAs and Their Potential Target Genes in Breast Cancer.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Jan;195(1):283-297. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04151-9. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36074234
-
Tumor microRNA expression profiling identifies circulating microRNAs for early breast cancer detection.Clin Chem. 2015 Aug;61(8):1098-106. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.238691. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 26056355
-
MicroRNAs and Extracellular Vesicles as Distinctive Biomarkers of Precocious and Advanced Stages of Breast Cancer Brain Metastases Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5214. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105214. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069135 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Circulating MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Efficacy Biomarkers.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Apr;24(2):153-173. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00447-w. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32067191 Review.
-
Exploring the Potential Role of Circulating microRNAs as Biomarkers for Predicting Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 10;24(12):9984. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129984. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disrupting Cell Cycle Machinery: CREPT Is an Emerging Target in Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 19;17(14):2401. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142401. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma miR-145-5p Levels and Risk of Future Cancer-Results from the HUNT Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2191. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052191. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076809 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the roles of non-coding RNAs in liposarcoma development: Challenges and opportunities for translational therapeutic advances.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Nov 15;11:73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.11.005. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39736850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pilot Study on the Analysis of Circulating miRNA Upregulation in Laryngeal Cancer.Diseases. 2025 Mar 30;13(4):101. doi: 10.3390/diseases13040101. Diseases. 2025. PMID: 40277812 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent and novel changes in plasma microRNA profiles in patients with non-small cell lung cancer following tumour resection.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):677-706. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-626. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40248723 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

