Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Modulation in a Rat Model for Ulcerative Colitis after the Intraperitoneal Administration of Apigenin, Luteolin, and Xanthohumol
- PMID: 38542210
- PMCID: PMC10970206
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063236
Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Modulation in a Rat Model for Ulcerative Colitis after the Intraperitoneal Administration of Apigenin, Luteolin, and Xanthohumol
Abstract
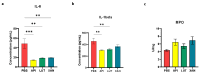
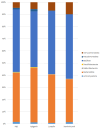
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the colon, with symptomatology influenced by factors including environmental, genomic, microbial, and immunological interactions. Gut microbiota dysbiosis, characterized by bacterial population alterations, contributes to intestinal homeostasis disruption and aberrant immune system activation, thereby exacerbating the inflammatory state. This study assesses the therapeutic efficacy of intraperitoneal (IP) injected flavonoids (apigenin, luteolin, and xanthohumol) in the reduction of inflammatory parameters and the modulation of the gut microbiota in a murine model of ulcerative colitis. Flavonoids interact with gut microbiota by modulating their composition and serving as substrates for the fermentation into other anti-inflammatory bioactive compounds. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of luteolin and xanthohumol treatment in enhancing the relative abundance of anti-inflammatory microorganisms, thereby attenuating pro-inflammatory species. Moreover, all three flavonoids exhibit efficacy in the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, with luteolin strongly demonstrating utility in alleviating associated physical UC symptoms. This suggests that this molecule is a potential alternative or co-therapy to conventional pharmacological interventions, potentially mitigating their adverse effects. A limited impact on microbiota is observed with apigenin, and this is attributed to its solubility constraints via the chosen administration route, resulting in its accumulation in the mesentery.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; flavonoid; gut microbiota; inflammatory bowel disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data, the writing of the manuscript, or the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Luteolin Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Plasma Metabolism.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 7;17(2):203. doi: 10.3390/nu17020203. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861331 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin alleviates inflammation and modulates gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis rats.Life Sci. 2021 Mar 15;269:119008. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119008. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33434535
-
Lonicera rupicola Hook.f.et Thoms flavonoids ameliorated dysregulated inflammatory responses, intestinal barrier, and gut microbiome in ulcerative colitis via PI3K/AKT pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154284. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154284. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35777121
-
Dietary flavonoids-microbiota crosstalk in intestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis.J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Mar;125:109494. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109494. Epub 2023 Oct 20. J Nutr Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37866426 Review.
-
Unraveling the microbial mysteries: gut microbiota's role in ulcerative colitis.Front Nutr. 2025 Feb 10;12:1519974. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1519974. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39996003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Response Surface Methodology to Design and Optimize Purification of Acetone or Aqueous Acetone Extracts of Hop Cones (Humulus lupulus L.) Using Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Xanthohumol Isolation.Materials (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;17(19):4827. doi: 10.3390/ma17194827. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39410398 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota, Circulating Metabolites and Risk of Endometriosis: A Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study.Pol J Microbiol. 2024 Dec 13;73(4):491-503. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2024-041. eCollection 2024 Dec 1. Pol J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39670637 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evidence for luteolin in ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1639644. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1639644. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40808687 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of honeysuckle flower in inflammatory bowel disease.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 28;12:1525675. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1525675. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40225345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;20(14):5608-5672. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.98107. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

