A Molecular Perspective on HIF-1α and Angiogenic Stimulator Networks and Their Role in Solid Tumors: An Update
- PMID: 38542288
- PMCID: PMC10970012
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063313
A Molecular Perspective on HIF-1α and Angiogenic Stimulator Networks and Their Role in Solid Tumors: An Update
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a major transcriptional factor, which plays an important role in cellular reprogramming processes under hypoxic conditions, which facilitate solid tumors' progression. HIF-1α is directly involved in the regulation of the angiogenesis, metabolic reprogramming, and extracellular matrix remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, an in-depth study on the role of HIF-1α in solid tumor malignancies is required to develop novel anti-cancer therapeutics. HIF-1α also plays a critical role in regulating growth factors, such as the vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and platelet-derived growth factor, in a network manner. Additionally, it plays a significant role in tumor progression and chemotherapy resistance by regulating a variety of angiogenic factors, including angiopoietin 1 and angiopoietin 2, matrix metalloproteinase, and erythropoietin, along with energy pathways. Therefore, this review attempts to provide comprehensive insight into the role of HIF-1α in the energy and angiogenesis pathways of solid tumors.
Keywords: HIF-1α; VEGF; angiogenesis; angiopoietins; hypoxia; solid tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
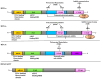

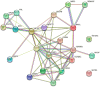
References
-
- Kulothungan V., Sathishkumar K., Leburu S., Ramamoorthy T., Stephen S., Basavarajappa D., Tomy N., Mohan R., Menon G.R., Mathur P. Burden of cancers in India—Estimates of cancer crude incidence, YLLs, YLDs and DALYs for 2021 and 2025 based on National Cancer Registry Program. BMC Cancer. 2022;22:527. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09578-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

