Gastric Cancer in the Era of Epigenetics
- PMID: 38542354
- PMCID: PMC10970362
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063381
Gastric Cancer in the Era of Epigenetics
Abstract
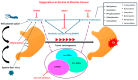
Gastric cancer (GC) remains a significant contributor to cancer-related mortality. Novel high-throughput techniques have enlightened the epigenetic mechanisms governing gene-expression regulation. Epigenetic characteristics contribute to molecular taxonomy and give rise to cancer-specific epigenetic patterns. Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection has an impact on aberrant DNA methylation either through its pathogenic CagA protein or by inducing chronic inflammation. The hypomethylation of specific repetitive elements generates an epigenetic field effect early in tumorigenesis. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection triggers DNA methylation by dysregulating DNA methyltransferases (DNMT) enzyme activity, while persistent Hp-EBV co-infection leads to aggressive tumor behavior. Distinct histone modifications are also responsible for oncogene upregulation and tumor-suppressor gene silencing in gastric carcinomas. While histone methylation and acetylation processes have been extensively studied, other less prevalent alterations contribute to the development and migration of gastric cancer via a complex network of interactions. Enzymes, such as Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), which is involved in tumor's metabolic reprogramming, interact with methyltransferases and modify gene expression. Non-coding RNA molecules, including long non-coding RNAs, circular RNAs, and miRNAs serve as epigenetic regulators contributing to GC development, metastasis, poor outcomes and therapy resistance. Serum RNA molecules hold the potential to serve as non-invasive biomarkers for diagnostic, prognostic or therapeutic applications. Gastric fluids represent a valuable source to identify potential biomarkers with diagnostic use in terms of liquid biopsy. Ongoing clinical trials are currently evaluating the efficacy of next-generation epigenetic drugs, displaying promising outcomes. Various approaches including multiple miRNA inhibitors or targeted nanoparticles carrying epigenetic drugs are being designed to enhance existing treatment efficacy and overcome treatment resistance.
Keywords: DNA methylation; epidrugs; epigenetics; gastric cancer; histone modifications; miRNAs; non-coding RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

