Pharmacological Activities, Therapeutic Effects, and Mechanistic Actions of Trigonelline
- PMID: 38542359
- PMCID: PMC10970276
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063385
Pharmacological Activities, Therapeutic Effects, and Mechanistic Actions of Trigonelline
Abstract
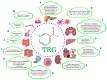
Trigonelline (TRG) is a natural polar hydrophilic alkaloid that is found in many plants such as green coffee beans and fenugreek seeds. TRG potentially acts on multiple molecular targets, including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, glycogen synthase kinase, tyrosinase, nerve growth factor, estrogen receptor, amyloid-β peptide, and several neurotransmitter receptors. In this review, we systematically summarize the pharmacological activities, medicinal properties, and mechanistic actions of TRG as a potential therapeutic agent. Mechanistically, TRG can facilitate the maintenance and restoration of the metabolic homeostasis of glucose and lipids. It can counteract inflammatory constituents at multiple levels by hampering pro-inflammatory factor release, alleviating inflammatory propagation, and attenuating tissue injury. It concurrently modulates oxidative stress by the blockage of the detrimental Nrf2 pathway when autophagy is impaired. Therefore, it exerts diverse therapeutic effects on a variety of pathological conditions associated with chronic metabolic diseases and age-related disorders. It shows multidimensional effects, including neuroprotection from neurodegenerative disorders and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, neuromodulation, mitigation of cardiovascular disorders, skin diseases, diabetic mellitus, liver and kidney injuries, and anti-pathogen and anti-tumor activities. Further validations are required to define its specific targeting molecules, dissect the underlying mechanistic networks, and corroborate its efficacy in clinical trials.
Keywords: chronic metabolic diseases; inflammation; metabolic homeostasis; neuromodulation; oxidation; trigonelline.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Elaine G. Taine works for TritaliMed, Inc. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Johns E. Ueber die alkaloide des bockshornsamens. Berdeutchem. Ges. 1885;15:2518–2523. doi: 10.1002/cber.188501802144. - DOI
-
- Taguchi H., Sakaguchi M., Shimabayashi Y. Trigonelline content in coffee beans and the thermal conversion of trigonelline into nicotinic acid during the roasting of coffee beans. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985;49:3467–3471.
-
- Ashihara H. Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2015. Chapter 3—Plant biochemistry: Trigonelline biosynthesis in coffea arabica and coffea canephora.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

