Dietary Adequacy in Older Adult Nursing Home Residents of the Northern Iberian Peninsula
- PMID: 38542709
- PMCID: PMC10975773
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16060798
Dietary Adequacy in Older Adult Nursing Home Residents of the Northern Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
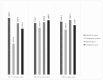
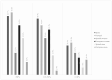
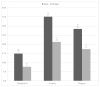
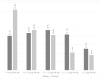
According to the latest data, Spain (19.4%) and Portugal (21.8%) are the two European countries with the highest percentage of older adults. Concerns about diet quality are increasing, especially among institutionalized older people, who are at the greatest risk of malnutrition. To assess the adequacy of dietary intake of 186 older adults (>65 y) institutionalized in public nursing homes (NH) in Galicia (Northwest Spain) and the Porto district (Northern Portugal), a cross-sectional study has been carried out. The double-weighing method and a country-specific food composition database were employed for nutritional assessment. Nutritional adequacy was assessed based on the recommendations of the EFSA and WHO. Caloric intake in Spanish NHs was higher than in Portuguese facilities; 20.3% and 35.8% of Spanish and Portuguese residents, respectively, had a protein intake below the EFSA recommendation, and 46.2% and 44.9% of residents in Portugal and Spain, respectively, had lipid intakes below the reference intake range. Further, 45.5% of the residents in Portugal and 66.9% in Spain had a carbohydrate intake within the recommended range. Salt intake was higher than the recommendation for 67.0% and 32.3% of the residents in Spain and Portugal, respectively. This study supports the notion that institutionalized older adults are prone to significant nutritional inadequacies.
Keywords: dietary intake; nursing homes; nutritional adequacy; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Who receives oral nutritional supplements in nursing homes? Results from the nutritionDay project.Clin Nutr. 2017 Oct;36(5):1360-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27692932
-
Malnutrition Prevalence and Nutrient Intakes of Indonesian Older Adults in Institutionalized Care Setting: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies.Ann Nutr Metab. 2024;80(5):235-252. doi: 10.1159/000538790. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Ann Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 38636475 Free PMC article.
-
Too low protein and energy intake in nursing home residents.Nutrition. 2023 Jun;110:112005. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2023.112005. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Nutrition. 2023. PMID: 36966585
-
An Even Distribution of Protein Intake Daily Promotes Protein Adequacy but Does Not Influence Nutritional Status in Institutionalized Elderly.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018 Jan;19(1):33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Nov 22. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29174562
-
Nutritional challenges for older adults in Europe: current status and future directions.Proc Nutr Soc. 2019 May;78(2):221-233. doi: 10.1017/S0029665118002744. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Proc Nutr Soc. 2019. PMID: 30696516 Review.
References
-
- Pérez-Díaz J., Ramiro-Farinas D., Aceituno-Nieto P., Díaz C.M., Clara, López B., Ruiz-Santacruz J.S., Morales I.F., Belmonte A.B.C., de las Obras-Loscertales Sampériz J., et al. Un Perfil de las Personas Mayores en España, 2022. Indicadores Estadísticos Básicos. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC). Centro de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales (CCHS). Envejecimiento en Red. 2022. Informes Envejecimiento en Red No. 29, 40p. [(accessed on 12 October 2022)]. Available online: http://envejecimiento.csic.es/documentos/documentos/enred-indicadoresbas....
-
- Oliveira A., Araújo J., Severo M., Correia D., Ramos E., Torres D., Lopes C., the IAN-AF Consortium Prevalence of general and abdominal obesity in Portugal: Comprehensive results from the National Food, nutrition and physical activity survey 2015–2016. BMC Public Health. 2018;18:614. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5480-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fávaro-Moreira N.C., Krausch-Hofmann S., Matthys C., Vereecken C., Vanhauwaert E., Declercq A., Bekkering G.E., Duyck J. Risk Factors for Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature Based on Longitudinal Data. Adv. Nutr. 2016;7:507–522. doi: 10.3945/an.115.011254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

