Functional and Therapeutic Potential of Cynara scolymus in Health Benefits
- PMID: 38542782
- PMCID: PMC10974306
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16060872
Functional and Therapeutic Potential of Cynara scolymus in Health Benefits
Abstract
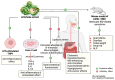
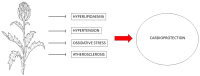
Dietary supplements enriched with bioactive compounds represent a promising approach to influence physiological processes and enhance longevity and overall health. Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus serves as a functional food supplement with a high concentration of bioactive compounds, which offers various health-promoting benefits. Several chronic diseases have metabolic, genetic, or inflammatory origins, which are frequently interconnected. Pharmacological treatments, although effective, often result in undesirable side effects. In this context, preventive approaches are gaining increased attention. Recent literature indicates that the consumption of bioactive compounds in the diet can positively influence the organism's biological functions. Polyphenols, well-known for their health benefits, are widely recognized as valuable compounds in preventing/combating various pathologies related to lifestyle, metabolism, and aging. The C. scolymus belonging to the Asteraceae family, is widely used in the food and herbal medicine fields for its beneficial properties. Although the inflorescences (capitula) of the artichoke are used for food and culinary purposes, preparations based on artichoke leaves can be used as an active ingredient in herbal medicines. Cynara scolymus shows potential benefits in different domains. Its nutritional value and health benefits make it a promising candidate for improving overall well-being. C. scolymus exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, liver-protective, bile-expelling, antimicrobial, and lipid-lowering neuroprotective properties. Different studies demonstrate that oxidative stress is the leading cause of the onset and progression of major human health disorders such as cardiovascular, neurological, metabolic, and cancer diseases. The large amount of polyphenol found in C. scolymus has an antioxidant activity, enabling it to neutralize free radicals, preventing cellular damage. This reduces the subsequent risk of developing conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, these polyphenols demonstrate anti-inflammatory activity, which is closely associated with their antioxidant properties. As a result, C. scolymus has the potential to contribute to the treatment of chronic diseases, including intestinal disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative pathologies. The current review discussed the nutritional profiles, potential benefits, and pharmacological effects of C. scolymus.
Keywords: artichoke; functional food; inflammation; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Quiroz D. Cynara Cardunculus (Cardoon) CABI Compendium; Boston, MA, USA: 2022. p. 17584. - DOI
-
- Soares Mateus A.R., Pena A., Sendón R., Almeida C., Nieto G.A., Khwaldia K., Sanches Silva A. By-Products of Dates, Cherries, Plums and Artichokes: A Source of Valuable Bioactive Compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023;131:220–243. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.12.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

