Chemistry and Pharmacology of Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol
- PMID: 38542886
- PMCID: PMC10976172
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061249
Chemistry and Pharmacology of Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol
Abstract
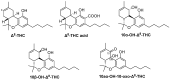
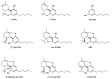
Cannabis sativa is one of the oldest plants utilized by humans for both economic and medical purposes. Although the use of cannabis started millennia ago in the Eastern hemisphere, its use has moved and flourished in the Western nations in more recent centuries. C. sativa is the source of psychoactive cannabinoids that are consumed as recreational drugs worldwide. The C21 aromatic hydrocarbons are restricted in their natural occurrence to cannabis (with a few exceptions). Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) is the main psychoactive component in cannabis, with many pharmacological effects and various approved medical applications. However, a wide range of side effects are associated with the use of Δ9-THC, limiting its medical use. In 1966, another psychoactive cannabinoid, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC) was isolated from marijuana grown in Maryland but in very low yield. Δ8-THC is gaining increased popularity due to its better stability and easier synthetic manufacturing procedures compared to Δ9-THC. The passing of the U.S. Farm Bill in 2018 led to an increase in the sale of Δ8-THC in the United States. The marketed products contain Δ8-THC from synthetic sources. In this review, methods of extraction, purification, and structure elucidation of Δ8-THC will be presented. The issue of whether Δ8-THC is a natural compound or an artifact will be discussed, and the different strategies for its chemical synthesis will be presented. Δ8-THC of synthetic origin is expected to contain some impurities due to residual amounts of starting materials and reagents, as well as side products of the reactions. The various methods of analysis and detection of impurities present in the marketed products will be discussed. The pharmacological effects of Δ8-THC, including its interaction with CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors in comparison with Δ9-THC, will be reviewed.
Keywords: analysis; chemistry; isolation; pharmacology; Δ8-THC.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Arno Hazekamp was employed by the company Hazekamp Herbal Consulting. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
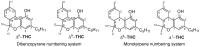

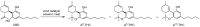

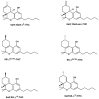
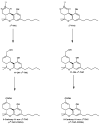
References
-
- Kriese U., Schumann E., Weber W., Beyer M., Brühl L., Matthäus Oil content, tocopherol composition and fatty acid patterns of the seeds of 51 Cannabis sativa L. genotypes. Euphytica. 2004;137:339–351. doi: 10.1023/B:EUPH.0000040473.23941.76. - DOI
-
- Doyle E., Spence A. Cannabis as a medicine? Br. J. Anaesth. 1995;74:359–361. - PubMed
-
- Gaoni Y., Mechoulam R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964;86:1646–1647. doi: 10.1021/ja01062a046. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

