Investigation of the Influence of Anti-Solvent Precipitation Parameters on the Physical Stability of Amorphous Solids
- PMID: 38542914
- PMCID: PMC10975851
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061275
Investigation of the Influence of Anti-Solvent Precipitation Parameters on the Physical Stability of Amorphous Solids
Abstract
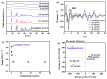
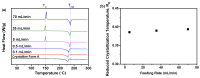
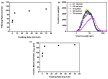
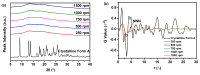
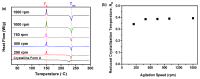
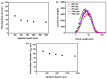
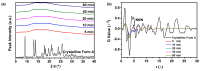
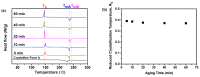
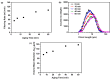
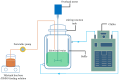
Amorphous solids exhibit enhanced solubility and dissolution rates relative to their crystalline counterparts. However, attaining optimal bioavailability presents a challenge, primarily due to the need to maintain the physical stability of amorphous solids. Moreover, the precise manner in which precipitation parameters, including the feeding rate of the anti-solvent, agitation speed, and aging time, influence the physical stability of amorphous solids remains incompletely understood. Consequently, this study aimed to investigate these three parameters during the precipitation process of the anticancer drug, nilotinib free base. The physical stability of the resultant samples was evaluated by employing characterization techniques including powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), focused beam reflectance measurement (FBRM), and data analysis methods such as pair distribution function (PDF), reduced crystallization temperature (Rc), and principal component analysis (PCA). This study's findings indicated that amorphous solids exhibited the greatest physical stability under particular conditions, namely a feeding rate of 5 mL/min, an agitation speed of 500 rpm, and an aging time of 10 min. Furthermore, the physical stability of the amorphous solids was primarily influenced by particle size and distribution, molecular interactions, microstructure, surface area, and interfacial energy. Notably, the parameters involved in the anti-solvent precipitation process, including the feeding rate of the anti-solvent, agitation speed, and aging time, exerted a significant impact on these factors. Consequently, they directly affected the physical stability of amorphous solids. Hence, this study comprehensively elucidated the mechanistic influence of these operational parameters on the physical stability of amorphous solids during the anti-solvent precipitation process.
Keywords: amorphous solid; pair distribution function; physical stability; principal component analysis; reduced crystallization temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Huzjak T., Jakasanovski O., Berginc K., Puž V., Zajc-Kreft K., Jeraj Ž., Janković B. Overcoming drug impurity challenges in amorphous solid dispersion with rational development of biorelevant dissolution-permeation method. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024;192:106655. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106655. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-González F., Herrera-González A.M., Donado F. Study of the transition from amorphous to crystalline phase in a granular system under shearing and vibration. Physica A. 2022;590:126756. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2021.126756. - DOI
-
- Dhaval M., Dudhat K., Soniwala M., Dudhrejiya A., Shah S., Prajapati B. A review on stabilization mechanism of amorphous form based drug delivery system. Mater. Today Commun. 2023;37:107411. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.107411. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

