Could the Length of the Alkyl Chain Affect the Photodynamic Activity of 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(1-alkylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrins?
- PMID: 38542921
- PMCID: PMC10974664
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061285
Could the Length of the Alkyl Chain Affect the Photodynamic Activity of 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(1-alkylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrins?
Abstract
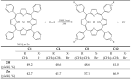
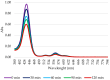
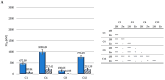
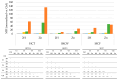
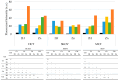
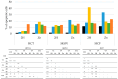
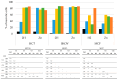
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive treatment that uses the combination of a photosensitizing agent (PS) and light to selectively target solid tumors, as well as several non-neoplastic proliferating cell diseases. After systemic administration, PSs are activated by localized irradiation with visible light; in the presence of adequate concentrations of molecular oxygen, this causes the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent tissue damage. In this study, two series of tetrakis(N-alkylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrins were synthesized, differing in the presence or absence of a zinc ion in the tetrapyrrole nucleus, as well as in the N-alkyl chain length (from one to twelve carbon atoms). The compounds were chemically characterized, and their effect on cell viability was evaluated using a panel of three tumor cell lines to determine a possible relationship between photodynamic activity and Zn presence/alkyl chain length. The types of cell death mechanisms involved in the effect of the various PSs were also evaluated. The obtained results indicate that the most effective porphyrin is the Zn-porphyrin, with a pendant made up of eight carbon atoms (Zn-C8).
Keywords: ROS; cell death mechanisms; cellular uptake; cytotoxicity; photodynamic therapy (PDT); tetrakis(N-alkylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrins; tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance of free-base and Zn(II) tricationic pyridiniumporphyrins and irradiation wavelength in PDT against the melanoma cell lines.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Jan 15;282:117063. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117063. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39566242
-
Synthesis and photodynamic activity of novel non-symmetrical diaryl porphyrins against cancer cell lines.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019 Jun;195:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 Apr 26. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019. PMID: 31075653
-
Amphiphilic cationic Zn-porphyrins with high photodynamic antimicrobial activity.Future Microbiol. 2015;10(5):709-24. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.148. Future Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26000647
-
Protein-Porphyrin Complex Photosensitizers for Anticancer and Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapies.ChemMedChem. 2023 Dec 1;18(23):e202300373. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300373. Epub 2023 Oct 27. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 37821798 Review.
-
Chemical approaches for the enhancement of porphyrin skeleton-based photodynamic therapy.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):1080-1099. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1755669. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32329382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can Porphyrin-Triphenylphosphonium Conjugates Enhance the Photosensitizer Performance Toward Bacterial Strains?ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Aug 19;7(8):5541-5552. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00659. Epub 2024 Jul 15. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 39008849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang L., Zhao S.J., Wu J.S., Yu L., Singh N., Yang K., Lan M.H., Wang P.F., Kim J.S. Photodynamic therapy for hypoxic tumors: Advances and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021;438:213888. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213888. - DOI
-
- Zhang Q., Li L. Photodynamic combinational therapy in cancer treatment. J. BUON. 2018;23:561–567. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

