Enzymatic Synthesis of New Acetoacetate-Ursodeoxycholic Acid Hybrids as Potential Therapeutic Agents and Useful Synthetic Scaffolds as Well
- PMID: 38542941
- PMCID: PMC10975173
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061305
Enzymatic Synthesis of New Acetoacetate-Ursodeoxycholic Acid Hybrids as Potential Therapeutic Agents and Useful Synthetic Scaffolds as Well
Abstract
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and acetoacetate are natural compounds present in the human intestine and blood, respectively. A number of studies highlighted that besides their well-known primary biological roles, both compounds possess the ability to influence a variety of cellular processes involved in the etiology of various diseases. These reasons suggested the potential of acetoacetate-UDCA hybrids as possible therapeutic agents and prompted us to develop a synthetic strategy to selectively derivatize the hydroxyl groups of the bile acid with acetoacetyl moieties. 3α-acetoacetoxy UDCA was obtained (60% isolated yield) via the regioselective transesterification of methyl acetoacetate with UDCA promoted by the Candida antarctica lipase B (CAL-B). 3α,7β-bis-acetoacetoxy UDCA was obtained instead by thermal condensation of methyl acetoacetate and UDCA (80% isolated yield). This bis-adduct was finally converted to the 7β-acetoacetoxy UDCA (82% isolated yield) via CAL-B catalyzed regioselective alcoholysis of the ester group on the 3α position. In order to demonstrate the value of the above new hybrids as UDCA-based scaffolds, 3α-acetoacetoxy UDCA was subjected to multicomponent Biginelli reaction with benzaldehyde and urea to obtain the corresponding 4-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-one derivative in 65% isolated yield.
Keywords: acetoacetate; biocatalysis; hybrid compounds; ketone bodies; lipase; ursodeoxycholic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
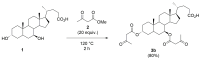
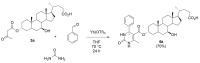
Similar articles
-
Effects of chemical modification of ursodeoxycholic acid on TGR5 activation.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(1):1-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21212509
-
Glyceric Prodrug of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA): Novozym 435-Catalyzed Synthesis of UDCA-Monoglyceride.Molecules. 2021 Oct 1;26(19):5966. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195966. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641510 Free PMC article.
-
delta 22-Ursodeoxycholic acid, a unique metabolite of administered ursodeoxycholic acid in rats, indicating partial beta-oxidation as a major pathway for bile acid metabolism.Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 4;34(13):4169-78. doi: 10.1021/bi00013a004. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 7703228
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: changes in maternal-fetal bile acid balance and improvement by ursodeoxycholic acid.Ann Hepatol. 2002 Jan-Mar;1(1):20-8. Ann Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 15114292 Review.
-
Hepatocellular bile acid transport and ursodeoxycholic acid hypercholeresis.Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Dec;34(12 Suppl):5S-15S. doi: 10.1007/BF01536656. Dig Dis Sci. 1989. PMID: 2689116 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Methods with Stereoselective Induction in the Asymmetric Biginelli Reaction.Molecules. 2024 Aug 15;29(16):3864. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163864. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

