Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Phenoxy Acetic Acid Derivatives as Selective COX-2 Inhibitors Coupled with Comprehensive Bio-Pharmacological Inquiry, Histopathological Profiling, and Toxicological Scrutiny
- PMID: 38542945
- PMCID: PMC10974743
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061309
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Phenoxy Acetic Acid Derivatives as Selective COX-2 Inhibitors Coupled with Comprehensive Bio-Pharmacological Inquiry, Histopathological Profiling, and Toxicological Scrutiny
Abstract
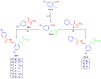
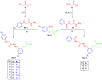
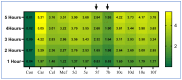
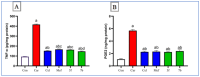
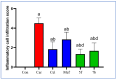
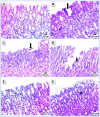
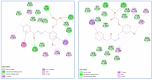
COX-2 plays a key role in converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. This makes it a significant target for treating inflammation. Selective COX-2 inhibitors have marked a new phase in inflammatory treatment, providing significant effectiveness while reducing negative side effects. Herein, we aimed at the design and synthesis of new anti-inflammatory agents 5a-f, 7a-b, 10a-f, and 13a-b with expected selective inhibition for COX-2. Compounds 5d-f, 7b, and 10c-f showed significant COX-2 inhibition with IC50 in the range of 0.06-0.09 μM, indicating powerful pharmacological potential. In light of this, eight compounds were selected for further testing in vivo to assess their selectivity toward COX-1/COX-2 enzymes with the ability to reduce paw thickness. Compounds 5f and 7b showed significant anti-inflammatory effects without causing stomach ulcers, as they showed significant in vivo inhibition for paw thickness at 63.35% and 46.51%, as well as paw weight at 68.26% and 64.84%. Additionally, the tested compounds lowered TNF-α by 61.04% and 64.88%, as well as PGE-2 by 60.58% and 57.07%, respectively. Furthermore, these potent compounds were thoroughly analyzed for their pain-relieving effects, histological changes, and toxicological properties. Assessing renal and stomach function, as well as measuring liver enzymes AST and ALT, together with kidney indicators creatinine and urea, offered valuable information on their safety profiles. Molecular modeling studies explain the complex ways in which the strong interacts with the COX-2 enzyme. This comprehensive strategy emphasizes the therapeutic potential and safety profiling of these new analogues for managing inflammation.
Keywords: COX-1/COX-2; PGE-2; anti-inflammatory; paw edema model; ulcerogenic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of novel and selective COX-2 inhibitors based on celecoxib scaffold supported with in vivo anti-inflammatory activity, ulcerogenic liability, ADME profiling and docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Mar;120:105627. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105627. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35065465
-
Optimization of pyrazole-based compounds with 1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol moiety as selective COX-2 inhibitors cardioprotective drug candidates: Design, synthesis, cyclooxygenase inhibition, anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenicity, cardiovascular evaluation, and molecular modeling studies.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Sep;114:105122. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105122. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34243075
-
Fenamates and ibuprofen as foundational components in the synthesis of innovative, targeted COX-2 anti-inflammatory drugs, undergoing thorough biopharmacological assessments and in-silico computational studies.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Jun;147:107393. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107393. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38691908
-
Novel tetrazole-based selective COX-2 inhibitors: Design, synthesis, anti-inflammatory activity, evaluation of PGE2, TNF-α, IL-6 and histopathological study.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104308. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104308. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33011534
-
Novel anti-inflammatory agents featuring phenoxy acetic acid moiety as a pharmacophore for selective COX-2 inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation, histopathological examination and molecular modeling investigation.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Nov;152:107727. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107727. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39167872
References
-
- Chen L., Deng H., Cui H., Fang J., Zuo Z., Deng J., Li Y., Wang X., Zhao L. Oncotarget 7204 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget. 2018;9:7204–7218. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

