A Thiourea Derivative of 2-[(1 R)-1-Aminoethyl]phenol as a Chiral Sensor for the Determination of the Absolute Configuration of N-3,5-Dinitrobenzoyl Derivatives of Amino Acids
- PMID: 38542955
- PMCID: PMC10974230
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061319
A Thiourea Derivative of 2-[(1 R)-1-Aminoethyl]phenol as a Chiral Sensor for the Determination of the Absolute Configuration of N-3,5-Dinitrobenzoyl Derivatives of Amino Acids
Abstract
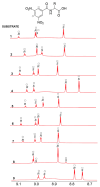
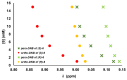
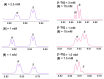
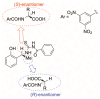
In the exploration of chiral solvating agents (CSAs) for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy designed for the chiral analysis of amino acid derivatives, notable advancements have been made with thiourea-CSAs. 1-TU, derived from 2-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]phenol and benzoyl isothiocyanate, is effective in the enantiodifferentiation of N-3,5-dinitrobenzoyl (N-DNB) amino acids. In order to broaden the application of 1-TU for configurational assignment, enantiomerically enriched N-DNB amino acids were analyzed via NMR. A robust correlation was established between the relative position of specific 1H and 13C NMR resonances of the enantiomers in the presence of 1-TU. 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO) was selected for the complete solubilization of amino acid substrates. Notably, the para and ortho protons of the N-DNB moiety displayed higher frequency shifts for the (R)-enantiomers as opposed to the (S)-enantiomers. This trend was consistently observed in the 13C NMR spectra for quaternary carbons bonded to NO2 groups. Conversely, an inverse correlation was noted for quaternary carbon resonances of the carboxyl moiety, amide carbonyl, and methine carbon at the chiral center. This observed trend aligns with the interaction mechanism previously reported for the same chiral auxiliary. The configurational correlation can be effectively exploited under conditions of high dilution or, significantly, under sub-stoichiometric conditions.
Keywords: NMR; chiral solvating agents; chirality; enantiodiscrimination; sense of nonequivalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
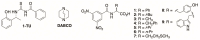

Similar articles
-
A Supramolecular Extension of Mosher's Method: Absolute Configuration Assignment of N-Amino Acid Derivatives via Bis-Thiourea Chiral Solvating Agent.Molecules. 2025 Jul 11;30(14):2930. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142930. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733196 Free PMC article.
-
Thiourea Derivative of 2-[(1R)-1-Aminoethyl]phenol: A Flexible Pocket-like Chiral Solvating Agent (CSA) for the Enantiodifferentiation of Amino Acid Derivatives by NMR Spectroscopy.J Org Chem. 2020 Apr 17;85(8):5342-5350. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00027. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Org Chem. 2020. PMID: 32191037 Free PMC article.
-
Isohexide-Based Tunable Chiral Platforms as Amide- and Thiourea-Chiral Solvating Agents for the NMR Enantiodiscrimination of Derivatized Amino Acids.Molecules. 2024 Mar 15;29(6):1307. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061307. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38542943 Free PMC article.
-
The Phenomenon of Self-Induced Diastereomeric Anisochrony and Its Implications in NMR Spectroscopy.Molecules. 2023 Sep 28;28(19):6854. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196854. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Multinuclear NMR Spectroscopy for Chiral Recognition of Organic Compounds.Molecules. 2017 Feb 7;22(2):247. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020247. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28178223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Supramolecular Extension of Mosher's Method: Absolute Configuration Assignment of N-Amino Acid Derivatives via Bis-Thiourea Chiral Solvating Agent.Molecules. 2025 Jul 11;30(14):2930. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142930. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dutot L., Wright K., Gaucher A., Wakselman M., Mazaleyrat J.-P., De Zotti M., Peggion C., Formaggio F., Toniolo C. The Bip Method, Based on the Induced Circular Dichroism of a Flexible Biphenyl Probe in Terminally Protected-Bip-Xaa*-Dipeptides, for Assignment of the Absolute Configuration of β-Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:5986–5992. doi: 10.1021/ja800059d. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

