Variation in the Composition and Quality of Nigella sativa L. Seed Oils-The Underestimated Impact on Possible Health-Promoting Properties
- PMID: 38542995
- PMCID: PMC10975171
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061360
Variation in the Composition and Quality of Nigella sativa L. Seed Oils-The Underestimated Impact on Possible Health-Promoting Properties
Abstract
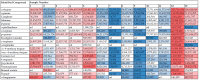
Nigella sativa L. (black cumin) is one of the most investigated medicinal plants in recent years. Volatile compounds like thymoquinone and unsaponifiable lipid compounds are crucial functional components of this oil. Unfortunately, the composition of oils and their quality indicators are ambiguous both in terms of identified compounds and value ranges. Thirteen oils were extracted with hexane from black cumin seeds grown in India, Syria, Egypt, and Poland and analyzed for their fatty acid composition, unsaponifiable compound content and volatile compounds. Oils were also subjected to quality tests according to standard methods. The fatty acid composition and sterol content/composition were relatively stable among the tested oils. Tocol content varied in the range of 140-631 mg/kg, and among them, β-tocotrienol and γ-tocopherol prevailed. Oils' volatile compounds were dominated by seven terpenes (p-cymene, α-thujene, α-pinene, β-pinene, thymoquinone, γ-terpinene, and sabinene). The highest contents of these volatiles were determined in samples from Poland and in two of six samples from India. High acid and peroxide values were typical features of N. sativa L. oils. To sum up, future research on the medicinal properties of black cumin oil should always be combined with the analysis of its chemical composition.
Keywords: Nigella sativa L.; black cumin; quality indices; thymoquinone; tocols; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Albakry Z., Karrar E., Ahmed I.A.M., Oz E., Proestos C., El Sheikha A.F., Oz F., Wu G., Wang X. Nutritional Composition and Volatile Compounds of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seed, Fatty Acid Composition and Tocopherols, Polyphenols, and Antioxidant Activity of Its Essential Oil. Horticulturae. 2022;8:575. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae8070575. - DOI
-
- Haron H., Grace-Lynn C., Shahar S. Comparison of Physicochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Activities of Nigella sativa Seeds and Oils from Yemen, Iran and Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2014;43:535–542.
-
- Salehi B., Quispe C., Imran M., Ul-Haq I., Živković J., Abu-Reidah I.M., Sen S., Taheri Y., Acharya K., Azadi H., et al. Nigella Plants—Traditional Uses, Bioactive Phytoconstituents, Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:625386. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.625386. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hossain M.S., Sharfaraz A., Dutta A., Ahsan A., Masud M.A., Ahmed I.A., Goh B.H., Urbi Z., Sarker M.M.R., Ming L.C. A Review of Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry, Antimicrobial Pharmacology and Toxicology of Nigella sativa L. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021;143:112182. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112182. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

