Potential Therapeutic Properties of Olea europaea Leaves from Selected Cultivars Based on Their Mineral and Organic Profiles
- PMID: 38543060
- PMCID: PMC10975974
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17030274
Potential Therapeutic Properties of Olea europaea Leaves from Selected Cultivars Based on Their Mineral and Organic Profiles
Abstract
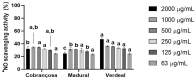
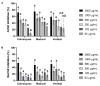
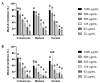
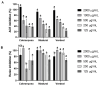
Olive leaves are consumed as an extract or as a whole herbal powder with several potential therapeutic benefits attributed to polyphenols, tocopherol's isomers, and flavonoids, among others. This study assessed the potential variance in the functional features presented by olive leaves from three different Portuguese cultivars-Cobrançosa, Madural, and Verdeal-randomly mix-cultivated in the geographical area of Vale de Salgueiros. Inorganic analysis determined their mineral profiles while an organic analysis measured their total phenolic and flavonoid content, and scanned their phenolic and tocopherol and fatty acid composition. The extracts' biological activity was tested by determining their antimicrobial and antioxidant power as well as their ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, MAO-A/B, and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. The inorganic profiles showed them to be an inexpensive source able to address different mineral deficiencies. All cultivars appear to have potential for use as possible antioxidants and future alternative antibiotics against some multidrug-resistant microorganisms, with caution regarding the arsenic content in the Verdeal cultivar. Madural's extract displayed properties to be considered a natural multitarget treatment for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, depression, and cardiometabolic and dual activity for blood pressure modulation. This work indicates that randomly cultivating different cultivars significantly modifies the leaves' composition while keeping their multifaceted therapeutic value.
Keywords: mineral and organic composition; olive tree leaves; therapeutic properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Updated Mineral Composition and Potential Therapeutic Properties of Different Varieties of Olive Leaves from Olea europaea.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;12(4):916. doi: 10.3390/plants12040916. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840264 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of olive storage period on oil quality of three Portuguese cultivars of Olea europea, Cobrançosa, Madural, and Verdeal Transmontana.J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Oct 23;50(22):6335-40. doi: 10.1021/jf011661y. J Agric Food Chem. 2002. PMID: 12381113
-
Updated Organic Composition and Potential Therapeutic Properties of Different Varieties of Olive Leaves from Olea europaea.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 3;12(3):688. doi: 10.3390/plants12030688. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771772 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols benefits of olive leaf (Olea europaea L) to human health.Nutr Hosp. 2014 Dec 17;31(3):1427-33. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.31.3.8400. Nutr Hosp. 2014. PMID: 25726243 Review.
-
[Research progress on biological activities of Olea europaea leaf extract].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;41(4):613-618. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20160411. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28871681 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
An integrated approach using morphological, biochemical, and RAPD markers to assess the genetic diversity of Olive (Olea Europaea L.) cultivars in India.Sci Rep. 2025 May 28;15(1):18664. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02815-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40436990 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Olive Oil Components on the Expression of Genes Related to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 3;17(3):570. doi: 10.3390/nu17030570. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Waste to Resource: Chemical Characterization of Olive Oil Industry By-Products for Sustainable Applications.Molecules. 2025 Jul 31;30(15):3212. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153212. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Passeri V., Sammut C., Mifsud D., Domesi A., Stanzione V., Baldoni L., Mousavi S., Mariotti R., Pandolfi S., Cinosi N., et al. The Ancient Olive Trees (Olea europaea L.) of the Maltese Islands: A Rich and Unexplored Patrimony to Enhance Oliviculture. Plants. 2023;12:1988. doi: 10.3390/plants12101988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

