Dyslipidemia: A Narrative Review on Pharmacotherapy
- PMID: 38543075
- PMCID: PMC10975559
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17030289
Dyslipidemia: A Narrative Review on Pharmacotherapy
Abstract
Dyslipidemia plays a fundamental role in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. Current guidelines for treating dyslipidemia focus on low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C). Despite advances in the pharmacotherapy of atherosclerosis, the most successful agents used to treat this disease-statins-remain insufficient in the primary or secondary prevention of acute myocardial infarction. Advancing therapy for hypercholesterolemia with emerging new drugs, either as monotherapy or in combination, is expected to improve cardiovascular outcomes. An emerging field in dyslipidemia pharmacotherapy is research on genetic therapies and genetic modulation. Understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying lipid alterations may lead to the development of personalized treatments that directly target the genetic causes of dyslipidemia. RNA messenger (mRNA)-based therapies are also being explored, offering the ability to modulate gene expression to normalize lipid levels. Furthermore, nanotechnology raises new possibilities in drug delivery for treating dyslipidemia. Controlled-release systems, nanoparticles, and liposomes can enhance the effectiveness and safety of medications by providing more precise and sustained release. This narrative review summarizes current and emerging therapies for the management of patients with dyslipidemia.
Keywords: cholesterol; dyslipidemias; gene therapy; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
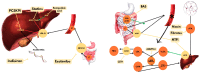

References
-
- McConnachie A., Walker A., Robertson M., Marchbank L., Peacock J., Packard C.J., Cobbe S.M., Ford I. Long-term impact on healthcare resource utilization of statin treatment, and its cost effectiveness in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A record linkage study. Eur. Heart J. 2014;35:290–298. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht232. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heller D.J., Coxson P.G., Penko J., Pletcher M.J., Goldman L., Odden M.C., Kazi D.S., Bibbins-Domingo K. Evaluating the Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Statin Use Guidelines for Primary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke. Circulation. 2017;136:1087–1098. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027067. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang M., Liu J., Bellows B.K., Qi Y., Sun J., Liu J., Moran A.E., Zhao D. Impact of China’s Low Centralized Medicine Procurement Prices on the Cost -Effectiveness of Statins for the Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Glob. Heart. 2020;15:43. doi: 10.5334/gh.830. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

