Identification and Development of BRD9 Chemical Probes
- PMID: 38543178
- PMCID: PMC10976250
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17030392
Identification and Development of BRD9 Chemical Probes
Abstract
The development of BRD9 inhibitors involves the design and synthesis of molecules that can specifically bind the BRD9 protein, interfering with the function of the chromatin-remodeling complex ncBAF, with the main advantage of modulating gene expression and controlling cellular processes. Here, we summarize the work conducted over the past 10 years to find new BRD9 binders, with an emphasis on their structure-activity relationships, efficacies, and selectivities in preliminary studies. BRD9 is expressed in a variety of cancer forms, hence, its inhibition holds particular significance in cancer research. However, it is crucial to note that the expanding research in the field, particularly in the development of new degraders, may uncover new therapeutic potentials.
Keywords: BRD9; PROTACs; drug discovery; inhibitors; leukemia; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures













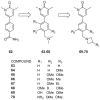






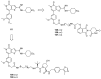






References
-
- Filippakopoulos P., Picaud S., Mangos M., Keates T., Lambert J.-P., Barsyte-Lovejoy D., Felletar I., Volkmer R., Müller S., Pawson T., et al. Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell. 2012;149:214–231. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

