Medication Lubricants for Oral Delivery of Drugs: Oral Processing Reduces Thickness, Changes Characteristics, and Improves Dissolution Profile
- PMID: 38543311
- PMCID: PMC10976129
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030417
Medication Lubricants for Oral Delivery of Drugs: Oral Processing Reduces Thickness, Changes Characteristics, and Improves Dissolution Profile
Abstract
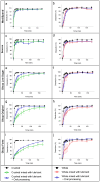
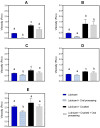
Swallowing oral solid dosage forms is challenging for those who have medication swallowing difficulties, including patients with dysphagia. One option is to mix the drug (whole or crushed) with a thick vehicle (medication lubricant). Previous in vitro studies consistently suggest that thick vehicles could impact the dissolution of solid dosage forms, potentially influencing their therapeutic effectiveness, but do not account for changes that happen during oral processing and swallowing. This study aims to investigate the potential impact of medication lubricants on drug release and examine the effect of oral processing. In vitro dissolution of whole and crushed paracetamol tablets mixed with five commercially available medication lubricants (two IDDSI level 2, two IDDSI level 3, and one IDDSI level 4) were tested with and without oral processing; a medication lubricant with/without paracetamol was placed in the mouth (five healthy volunteers), prepared for swallowing, but then expectorated and assessed for physical characteristics and drug release. Medication lubricants, both alone and mixed with crushed paracetamol tablets, showed a significant decrease in viscosity after oral processing. Without oral processing, IDDSI level 3 and 4 lubricants significantly delayed the dissolution of paracetamol tablets. After oral processing, particularly with crushed tablets, there was a substantial increase in the dissolution rate. These findings suggest that dissolution testing overestimates the impact of medication lubricants on drug dissolution. Therefore, using in vitro dissolution tests to predict the dissolution rate of medications mixed with thick vehicles is discouraged. It is essential to consider ways to incorporate the effects of the oral environment and oral processing on thick vehicles used for oral medication administration.
Keywords: carrageenan; cellulose gum; chromophore; polysaccharide; rheology; xanthan gum; yield stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Medication Swallowing Lubricants Suitable for Use in Dysphagia? Consistency, Viscosity, Texture, and Application of the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI) Framework.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Sep 28;12(10):924. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12100924. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32998301 Free PMC article.
-
Oral medication delivery in impaired swallowing: thickening liquid medications for safe swallowing alters dissolution characteristics.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016 Sep;42(9):1537-44. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2016.1151033. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26857812
-
Crushed tablets: does the administration of food vehicles and thickened fluids to aid medication swallowing alter drug release?J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;17(2):207-19. doi: 10.18433/j39w3v. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24934549
-
Crushed Tablet Administration for Patients with Dysphagia and Enteral Feeding: Challenges and Considerations.Drugs Aging. 2023 Oct;40(10):895-907. doi: 10.1007/s40266-023-01056-y. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Drugs Aging. 2023. PMID: 37707775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective analysis of the biopharmaceutics characteristics of solid oral Modified-Release drug products in approved US FDA NDAs designated as Extended-Release or Delayed-Release formulations.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023 Dec;193:294-305. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.11.014. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023. PMID: 37984592 Review.
References
-
- Buhmann C., Bihler M., Emich K., Hidding U., Pötter-Nerger M., Gerloff C., Niessen A., Flügel T., Koseki J.-C., Nienstedt J.C., et al. Pill Swallowing in Parkinson’s Disease: A Prospective Study Based on Flexible Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing. Park. Relat. D. 2019;62:51–56. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.02.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sopade P., Halley P., Cichero J., Ward L. Rheological Characterisation of Food Thickeners Marketed in Australia in Various Media for the Management of Dysphagia. I: Water and Cordial. J. Food Eng. 2007;79:69–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.01.045. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

