Synthesis and Properties of Injectable Hydrogel for Tissue Filling
- PMID: 38543325
- PMCID: PMC10975320
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030430
Synthesis and Properties of Injectable Hydrogel for Tissue Filling
Abstract
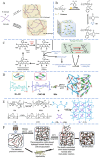
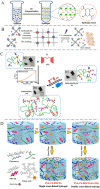
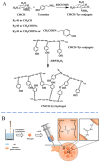
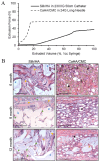
Hydrogels with injectability have emerged as the focal point in tissue filling, owing to their unique properties, such as minimal adverse effects, faster recovery, good results, and negligible disruption to daily activities. These hydrogels could attain their injectability through chemical covalent crosslinking, physical crosslinking, or biological crosslinking. These reactions allow for the formation of reversible bonds or delayed gelatinization, ensuring a minimally invasive approach for tissue filling. Injectable hydrogels facilitate tissue augmentation and tissue regeneration by offering slow degradation, mechanical support, and the modulation of biological functions in host cells. This review summarizes the recent advancements in synthetic strategies for injectable hydrogels and introduces their application in tissue filling. Ultimately, we discuss the prospects and prevailing challenges in developing optimal injectable hydrogels for tissue augmentation, aiming to chart a course for future investigations.
Keywords: hydrogel; injectability; tissue filling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A di-self-crosslinking hyaluronan-based hydrogel combined with type I collagen to construct a biomimetic injectable cartilage-filling scaffold.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jul 15;111:197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.007. Epub 2020 May 17. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32434079
-
Self-Healing Injectable Hydrogels for Tissue Regeneration.Chem Rev. 2023 Jan 25;123(2):834-873. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00179. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 35930422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based dual-crosslinking biohybrid injectable hydrogels for vascularization.Acta Biomater. 2020 Apr 15;107:138-151. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.041. Epub 2020 Mar 1. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32126310
-
Advances in bioactive glass-containing injectable hydrogel biomaterials for tissue regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2021 Dec;136:1-36. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.034. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34562661 Review.
-
Dual crosslinking hydrogels with tunable injectability and stability for bone repair.J Mater Chem B. 2022 Jun 15;10(23):4386-4394. doi: 10.1039/d2tb00545j. J Mater Chem B. 2022. PMID: 35616110
Cited by
-
Collagen and Its Derivatives Serving Biomedical Purposes: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 22;16(18):2668. doi: 10.3390/polym16182668. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-Drug Delivery Systems Using Hydrogel-Nanoparticle Composites: Recent Advances and Key Applications.Gels. 2025 Jul 3;11(7):520. doi: 10.3390/gels11070520. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40710682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable supramolecular hydrogel co-loading abemaciclib/NLG919 for neoadjuvant immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 15;16(1):687. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55904-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39814714 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a PLA Polymer-Based Liquid Filler for Next-Generation Aesthetics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 6;26(5):2369. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052369. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076988 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and characterization of bovine dental pulp-derived extracellular matrix hydrogel for regenerative endodontic applications: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 24;24(1):1281. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05004-z. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39448989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ralf Paus L., Berneburg M., Trelles M., Friguet B., Ogden S., Esrefoglu M., Kaya G., Goldberg D.J., Mordon S., Calderhead R.G., et al. How best to halt and/or revert UV-induced skin ageing: Strategies, facts and fiction. Exp. Dermatol. 2009;17:228–229. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82072060/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22008201/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- SWU-XDPY22006/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2205012980212766/Venture & Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees
- cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0292/Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

