Cellulose Nanofibrils-Reinforced Pectin Membranes for the Adsorption of Cationic Dyes from a Model Solution
- PMID: 38543330
- PMCID: PMC10975991
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16060724
Cellulose Nanofibrils-Reinforced Pectin Membranes for the Adsorption of Cationic Dyes from a Model Solution
Abstract
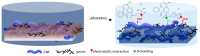
In the presented research, a facile, one-step method for the fabrication of cellulose nanofibrils/pectin (CNFs/PC) membranes is described, which were tested further for their ability to remove cationic dyes from the prepared model solutions. For this purpose, ten membranes were prepared with different quantities of CNFs and PC with/without citric acid (CA) or CaCl2 as mediated crosslinking agents, and they were characterised comprehensively in terms of their physical, chemical, and hydrophilic properties. All the prepared CNFs/PC membranes were hydrophilic with a Water Contact Angle (WCA) from 51.23° (without crosslinker) up to 78.30° (CaCl2) and swelling of up to 485% (without crosslinker), up to 437% (CaCl2) and up to 270% (CA). The stability of membranes was decreased with the increase in PC; thus, only four membranes (M1, M2, M3 and M5) were stable enough in water after 24 h, and these were additionally applied in the adsorption trials, using two structurally different cationic dyes, i.e., C.I. Basic Yellow 28 (BY28) and C.I. Basic Blue 22 (BB22), in four concentrations. The highest total surface charge of M3 (2.83 mmol/g) as compared to the other membranes influenced the maximal removal efficiency of both dyes, up to 37% (BY28) and up to 71% (BB22), depending on the initial dye concentration. The final characteristics of the membranes and, consequently, the dye's absorption ability could be tuned easily by changing the ratio between the CNFs and PC, as well as the type and amount of crosslinker.
Keywords: adsorption; cationic dyes; cellulose nanofibrils; dye removal; membrane; pectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
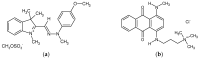






Similar articles
-
Efficiency of Differently Processed Membranes Based on Cellulose as Cationic Dye Adsorbents.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Mar 30;10(4):642. doi: 10.3390/nano10040642. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32235489 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorption of Basic Yellow 28 and Basic Blue 3 Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Silybum Marianum Stem as a Low-Cost Adsorbent.Molecules. 2023 Sep 15;28(18):6639. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186639. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764414 Free PMC article.
-
Turning calcium carbonate into a cost-effective wastewater-sorbing material by occluding waste dye.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010 Jan;17(1):97-105. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0111-y. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010. PMID: 19263103
-
Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using an efficient chitosan-pectin bio-adsorbent: kinetics and isotherm studies.Environ Monit Assess. 2023 Jan 27;195(2):339. doi: 10.1007/s10661-022-10900-4. Environ Monit Assess. 2023. PMID: 36705863
-
Using protein nanofibrils to remove azo dyes from aqueous solution by the coagulation process.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013 Dec 1;112:245-54. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013. PMID: 23999142
Cited by
-
Research Advances in Natural Polymers for Environmental Remediation.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;17(5):559. doi: 10.3390/polym17050559. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40076053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradable Cassava Starch/Phosphorite/Citric Acid Based Hydrogel for Slow Release of Phosphorus: In Vitro Study.Gels. 2024 Jun 28;10(7):431. doi: 10.3390/gels10070431. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39057454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ojstršek A., Fakin D. Layered compact textiles applied in fixed-bed column as filters for dye-rich textile wastewaters treatment—A case study. Des. Wat. Treat. 2013;51:3060–3068. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2012.748457. - DOI
-
- Tang Y., Hu T., Zeng Y., Zhou Q., Peng Y. Effective adsorption of cationic dyes by lignin sulfonate polymer based on simple emulsion polymerization: Isotherm and kinetic studies. RSC Adv. 2015;5:3757–3766. doi: 10.1039/C4RA12229A. - DOI
-
- Materials Market Report. [(accessed on 11 January 2024)]. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/app/uploads/2023/11/Materials-Market-Report-....
-
- Market Research Report. [(accessed on 11 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/acrylic-fiber-market-2125.
-
- Ojstršek A., Gorjanc N., Fakin D. Reduction of Lead and Antimony Ions from the Crystal Glass Wastewaters Utilising Adsorption. Sustainability. 2021;13:11156. doi: 10.3390/su132011156. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

