Genetic and Phenotypic Characterization of Bacillus velezensis Strain BV379 for Human Probiotic Applications
- PMID: 38543487
- PMCID: PMC10974050
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12030436
Genetic and Phenotypic Characterization of Bacillus velezensis Strain BV379 for Human Probiotic Applications
Abstract
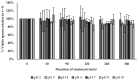
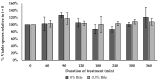
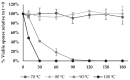
Bacterial spore-forming Bacillaceae species, including Bacillus subtilis and Heyndrickxia coagulans, are increasingly utilized for probiotic dietary supplementation. Bacillus velezensis is a Bacillus species that is frequently used as a direct-fed microbial in animal feed but less so as a probiotic for humans. The objective of this study was to characterize the suitability of the Bacillus velezensis strain BV379 for probiotic applications by (1) in silico screening for both adverse genetic elements and putatively beneficial traits, (2) in vitro evaluation of interactions with human intestinal epithelial cells, and (3) in vitro characterization of BV379 spore viability at various temperatures, pH, and in the presence of bile salt. In silico screening of the BV379 genome revealed few genes encoding Bacillaceae-associated toxins, virulence factors, and enzymes involved in the production of toxins. While BV379 encodes five antimicrobial resistance genes, minimum inhibitory concentration assays determined that BV379 is susceptible to all eight clinically relevant antibiotics tested. Preliminary cell culture experiments showed that BV379 lysates did not adversely impact human intestinal epithelial cell viability and monolayer permeability. It was also determined that BV379 spores can easily tolerate the harsh pH, bile salt, and microaerobic conditions typical of the GI tract. Altogether, the results presented herein support the safety and potential of Bacillus velezensis strain BV379 for use as an oral probiotic.
Keywords: BV379; Bacillus velezensis; endospore; probiotic; safety; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
L.M.B, S.G., and J.L.S. are employees of BIO-CAT Microbials, LLC, which provided funding and manufactured the
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Phenotypic Characterization and Genomic Analysis Unveil the Probiotic Potential of Bacillus velezensis K12.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 11;15(6):798. doi: 10.3390/ani15060798. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150327 Free PMC article.
-
Subchronic oral toxicity assessment of Bacillus velezensis strain BV379 in sprague-dawley rats.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024 Jan-Dec;43:9603271241278977. doi: 10.1177/09603271241278977. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39326930
-
Preclinical Safety Assessment of Bacillus subtilis BS50 for Probiotic and Food Applications.Microorganisms. 2022 May 17;10(5):1038. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10051038. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630480 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Bacillus velezensis as a probiotic in animal feed: a review.J Microbiol. 2021 Jul;59(7):627-633. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-1161-1. Epub 2021 Jul 1. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34212287 Review.
-
Bacillus strains as human probiotics: characterization, safety, microbiome, and probiotic carrier.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 8;28(5):1297-1305. doi: 10.1007/s10068-019-00691-9. eCollection 2019 Oct. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31695928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
First report of the agricultural biocontrol agent Bacillus velezensis and foodborne outbreak due to rope spoilage in cakes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Apr 23;91(4):e0257024. doi: 10.1128/aem.02570-24. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40152609 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico and In Vitro Characterization of Bacillus velezensis P45: Screening for a Novel Probiotic Candidate.Foods. 2025 Jun 30;14(13):2334. doi: 10.3390/foods14132334. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647086 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling the resistome and virulome of Bacillus strains used for probiotic-based sanitation: a multicenter WGS analysis.BMC Genomics. 2025 Apr 18;26(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11582-1. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40251489 Free PMC article.
-
The research on the identification, taxonomy, and comparative genomics analysis of nine Bacillus velezensis strains significantly contributes to microbiology, genetics, bioinformatics, and biotechnology.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1544934. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1544934. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40177483 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Phenotypic Characterization and Genomic Analysis Unveil the Probiotic Potential of Bacillus velezensis K12.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 11;15(6):798. doi: 10.3390/ani15060798. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harwood C.R. Bacillus. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 1989. Introduction to the Biotechnology of Bacillus; pp. 1–4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

