Recent Advances on Targeting Proteases for Antiviral Development
- PMID: 38543732
- PMCID: PMC10976044
- DOI: 10.3390/v16030366
Recent Advances on Targeting Proteases for Antiviral Development
Abstract
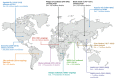
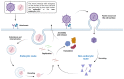
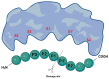
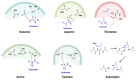
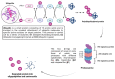
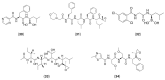
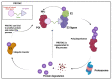
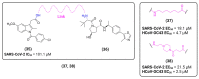
Viral proteases are an important target for drug development, since they can modulate vital pathways in viral replication, maturation, assembly and cell entry. With the (re)appearance of several new viruses responsible for causing diseases in humans, like the West Nile virus (WNV) and the recent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), understanding the mechanisms behind blocking viral protease's function is pivotal for the development of new antiviral drugs and therapeutical strategies. Apart from directly inhibiting the target protease, usually by targeting its active site, several new pathways have been explored to impair its activity, such as inducing protein aggregation, targeting allosteric sites or by inducing protein degradation by cellular proteasomes, which can be extremely valuable when considering the emerging drug-resistant strains. In this review, we aim to discuss the recent advances on a broad range of viral proteases inhibitors, therapies and molecular approaches for protein inactivation or degradation, giving an insight on different possible strategies against this important class of antiviral target.
Keywords: PROTACs; antiviral therapies; covalent inhibitors; natural products; peptidomimetics; viral proteases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
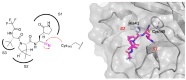
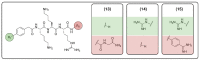
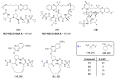

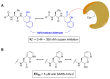
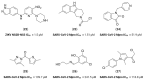
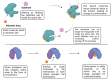
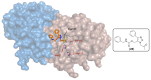
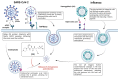
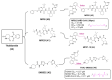
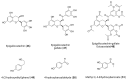
References
-
- Kaiwan O., Sethi Y., Khehra N., Padda I., Chopra H., Chandran D., Dhama K., Chakraborty C., Islam A., Kaka N. Emerging and re-emerging viral diseases, predisposing risk factors, and implications of international travel: A call for action for increasing vigilance and imposing restrictions under the current threats of recently emerging multiple Omicron subvariants. Int. J. Surg. 2023;109:589–591. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000176. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

