mRNA Therapeutic Vaccine for Hepatitis B Demonstrates Immunogenicity and Efficacy in the AAV-HBV Mouse Model
- PMID: 38543871
- PMCID: PMC10976109
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12030237
mRNA Therapeutic Vaccine for Hepatitis B Demonstrates Immunogenicity and Efficacy in the AAV-HBV Mouse Model
Abstract
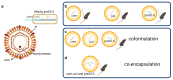
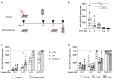
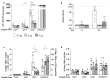
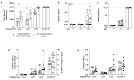
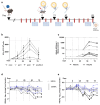
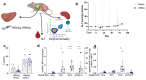
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) develops in millions of patients per year, despite the availability of effective prophylactic vaccines. Patients who resolve acute HBV infection develop HBV-specific polyfunctional T cells accompanied by neutralizing antibodies, while in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), immune cells are dysfunctional and impaired. We describe a lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-formulated mRNA vaccine, optimized for the expression of HBV core, polymerase, and surface (preS2-S) antigens with the aim of inducing an effective immune response in patients with CHB. Prime and prime/boost vaccination with LNP-formulated mRNA encoding for core, pol, and/or preS2-S dosing strategies were compared in naive C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. Immune responses were assessed by IFN-γ ELISpot, intracellular cytokine staining (ICS), and ELISA for antibody production, whereas anti-viral efficacy was evaluated in the AAV-HBV mouse model. The mRNA vaccine induced strong antigen-specific polyfunctional T cell responses in these mouse models, accompanied by the emergence of anti-HBs and anti-HBe antibodies. After three immunizations, the antigen-specific immune stimulation resulted in up to 1.7 log10 IU/mL reduction in systemic HBV surface antigen (HBsAg), accompanied by a transient drop in systemic HBeAg, and this was observed in 50% of the AAV-HBV-transduced mice in the absence of additional modalities such as adjuvants, HBsAg reducing agents, or checkpoint inhibitors. However, no treatment-related effect on viremia was observed in the liver. These results warrant further optimization and evaluation of this mRNA vaccine as a candidate in a multimodal therapeutic regimen for the treatment of chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: AAV-HBV mice; HBsAg reduction; chronic hepatitis B; lipid nanoparticles; mRNA vaccine; therapeutic vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
D.D.P., B.D.C., I.N., H.D., E.V.G., S.P., and D.B. were employed by Janssen Research and Development at the time of the research and may be Johnson and Johnson stockholders. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Hepatitis B. [(accessed on 18 July 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

