Flublok Quadrivalent Vaccine Adjuvanted with R-DOTAP Elicits a Robust and Multifunctional CD4 T Cell Response That Is of Greater Magnitude and Functional Diversity Than Conventional Adjuvant Systems
- PMID: 38543915
- PMCID: PMC10975948
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12030281
Flublok Quadrivalent Vaccine Adjuvanted with R-DOTAP Elicits a Robust and Multifunctional CD4 T Cell Response That Is of Greater Magnitude and Functional Diversity Than Conventional Adjuvant Systems
Abstract
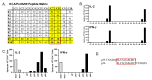
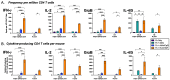
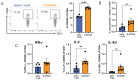
It is clear that new approaches are needed to promote broadly protective immunity to viral pathogens, particularly those that are prone to mutation and escape from antibody-mediated immunity. CD4+ T cells, known to target many viral proteins and highly conserved peptide epitopes, can contribute greatly to protective immunity through multiple mechanisms. Despite this potential, CD4+ T cells are often poorly recruited by current vaccine strategies. Here, we have analyzed a promising new adjuvant (R-DOTAP), as well as conventional adjuvant systems AddaVax with or without an added TLR9 agonist CpG, to promote CD4+ T cell responses to the licensed vaccine Flublok containing H1, H3, and HA-B proteins. Our studies, using a preclinical mouse model of vaccination, revealed that the addition of R-DOTAP to Flublok dramatically enhances the magnitude and functionality of CD4+ T cells specific for HA-derived CD4+ T cell epitopes, far outperforming conventional adjuvant systems based on cytokine EliSpot assays and multiparameter flow cytometry. The elicited CD4+ T cells specific for HA-derived epitopes produce IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-4/5, and granzyme B and have multifunctional potential. Hence, R-DOTAP, which has been verified safe by human studies, can offer exciting opportunities as an immune stimulant for next-generation prophylactic recombinant protein-based vaccines.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; adjuvants; hemagglutinin; influenza; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
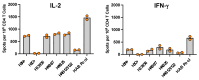

Similar articles
-
R-DOTAP Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles Outperform Squalene-Based Adjuvant Systems in Elicitation of CD4 T Cells after Recombinant Influenza Hemagglutinin Vaccination.Viruses. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):538. doi: 10.3390/v15020538. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851752 Free PMC article.
-
Broadly Protective CD8+ T Cell Immunity to Highly Conserved Epitopes Elicited by Heat Shock Protein gp96-Adjuvanted Influenza Monovalent Split Vaccine.J Virol. 2021 May 24;95(12):e00507-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00507-21. Print 2021 May 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33827939 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Protein Vaccines Formulated with Enantio-Specific Cationic Lipid R-DOTAP Induce Protective Cellular and Antibody-Mediated Immune Responses in Mice.Viruses. 2023 Feb 4;15(2):432. doi: 10.3390/v15020432. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851646 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Nanoparticle Vaccination Elicits a Persistent, Polyfunctional CD4 T Cell Response in the Murine Lung Specific for a Highly Conserved Influenza Virus Antigen That Is Sufficient To Mediate Protection from Influenza Virus Challenge.J Virol. 2021 Jul 26;95(16):e0084121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00841-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34076479 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Vaccination Directs the CD4+ T Cell Response toward Shared Protective Epitopes That Can Be Recalled after Influenza Virus Infection.J Virol. 2019 Sep 30;93(20):e00947-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00947-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31341045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Computationally Optimized Hemagglutinin Proteins Adjuvanted with Infectimune® Generate Broadly Protective Antibody Responses in Mice and Ferrets.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 2;12(12):1364. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121364. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Beltran W.F., Lam E.C., St Denis K., Nitido A.D., Garcia Z.H., Hauser B.M., Feldman J., Pavlovic M.N., Gregory D.J., Poznansky M.C., et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell. 2021;184:2372–2383.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

