Pilot Study on Evaluating the Impact of Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (Tdap), Influenza, and COVID-19 Vaccinations on Antibody Responses in Pregnant Women
- PMID: 38543946
- PMCID: PMC10974830
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12030312
Pilot Study on Evaluating the Impact of Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (Tdap), Influenza, and COVID-19 Vaccinations on Antibody Responses in Pregnant Women
Abstract
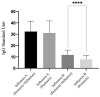
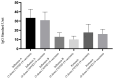
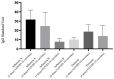
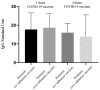
This study assessed IgG levels to influenza/pertussis and neutralizing antibody (Nab) responses of COVID-19 vaccines in blood of pregnant women following immunization with pertussis (Tdap), influenza, and COVID-19 vaccines. We prospectively collected 71 participants categorized by the following vaccine combinations: 3TI, 4TI, 3T, and 4T groups (three and four doses of COVID-19 vaccines plus Tdap/influenza or Tdap vaccines alone). Our findings have indicated that the 3TI group exhibited elevated IgG levels for influenza B compared to the 3T group (12.90 vs. 7.75 U, p = 0.001); this pattern was not observed for influenza A. Pertussis IgG levels remained uniform across all groups. The 4TI group demonstrated a greater Nab inhibition rate from COVID-19 vaccines compared to both the 3TI and 3T groups (61.34% vs. 22.5% and 15.16%, respectively, p = 0.001). We observed no correlation between Nab inhibition rate and IgG levels for Tdap/influenza, with the exception of a moderate correlation with influenza B in the 3TI group. The efficacy of Tdap vaccine in pregnant women remained consistent, regardless of the administration of COVID-19 or influenza vaccines. Interestingly, without the influenza vaccine, both three and four doses of the COVID-19 vaccine still offered protection against influenza A, but not B. Hence, co-administering COVID-19, influenza, and Tdap vaccines during prenatal care maintains immunogenicity and is highly advised to safeguard pregnant women fully.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Nab; Tdap; influenza; maternal vaccination; neutralizing antibody; pertussis; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficiency of placental transfer of vaccine-elicited antibodies relative to prenatal Tdap vaccination status.Vaccine. 2020 Jun 26;38(31):4869-4876. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.036. Epub 2020 May 29. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32482459 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with Intention to Receive Influenza and Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Acellular Pertussis (Tdap) Vaccines during Pregnancy: A Focus on Vaccine Hesitancy and Perceptions of Disease Severity and Vaccine Safety.PLoS Curr. 2015 Feb 25;7:ecurrents.outbreaks.d37b61bceebae5a7a06d40a301cfa819. doi: 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.d37b61bceebae5a7a06d40a301cfa819. PLoS Curr. 2015. PMID: 25789203 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal pertussis vaccination and its effects on the immune response of infants aged up to 12 months in the Netherlands: an open-label, parallel, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Apr;19(4):392-401. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30717-5. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30938299 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria among pregnant and postpartum women and their infants recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008 May 30;57(RR-4):1-51. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008. PMID: 18509304 Review.
-
Factors associated with Tdap vaccination receipt during pregnancy: a cross-sectional study.Public Health. 2020 Feb;179:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31726399 Review.
Cited by
-
Adult Vaccine Coadministration Is Safe, Effective, and Acceptable: Results of a Survey of the Literature.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025 Mar;19(3):e70090. doi: 10.1111/irv.70090. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40045565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borges do Nascimento I.J., O’Mathúna D.P., von Groote T.C., Abdulazeem H.M., Weerasekara I., Marusic A., Puljak L., Civile V.T., Zakarija-Grkovic I., Pericic T.P., et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: An overview of systematic reviews. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021;21:525. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06214-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gurol-Urganci I., Jardine J.E., Carroll F., Draycott T., Dunn G., Fremeaux A., Harris T., Hawdon J., Morris E., Muller P., et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection at the time of birth in England: National cohort study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021;225:522.e1–522.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.05.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W.C., Lin Y.P., Cheng C.M., Shen C.F., Ching A., Chang T.C., Shen C.J. Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Variants in Pregnant Women and Their Neonates under Antenatal Vaccination with Moderna (mRNA-1273) Vaccine. Vaccines. 2022;10:1415. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10091415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

