Thermography Sensor to Assess Motor and Sensitive Neuromuscular Sequels of Brain Damage
- PMID: 38543986
- PMCID: PMC10974549
- DOI: 10.3390/s24061723
Thermography Sensor to Assess Motor and Sensitive Neuromuscular Sequels of Brain Damage
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to observe the validity, diagnostic capacity, and reliability of the thermographic technique in the analysis of sensitive and motor sequelae in patients with chronic brain damage.
Method: A longitudinal descriptive observational study was performed. Forty-five people with impairment in at least one anatomical region participated in and completed this study. All patients who had become infected by SARS-CoV-2 in the past year were excluded. Thermographic measurement was conducted, and the Modified Ashworth Scale and Pressure Pain Threshold was analyzed.
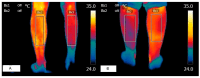
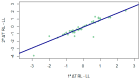
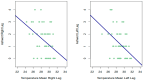
Results: A high correlation between two times of thermography data was observed. The Spearman correlations obtained between the Ashworth score on each leg and the temperature given by thermography were all significant.
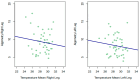
Discussion and conclusions: Despite the above, the Spearman correlations obtained between the PPT in each leg and the temperature offered by thermography were not significant in any of the measurements. For this reason, thermography is a potential tool for the diagnosis and assessment of neuromuscular motor sequelae, but not for sensitive sequelae, after brain injury. Nevertheless, for the time being, no statistical relationship has been observed between the data reported by thermography and PPT; thus, future studies are needed to further investigate these results.
Keywords: brain damage; neuromuscular diseases; stroke; thermography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship Between Infrared Thermography and Functional Parameters in the Lower Limbs of Hemiplegic Patients.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;15(4):542. doi: 10.3390/life15040542. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283098 Free PMC article.
-
Skin temperature assessment for neuromusculoskeletal abnormalities of the spinal column.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1992 Jul-Aug;15(6):365-81. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1992. PMID: 1431620 Review.
-
Intra- and inter-session reliability and repeatability of an infrared thermography device designed for materials to measure skin temperature of the triceps surae muscle tissue of athletes.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 9;11:e15011. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15011. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36919164 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and repeatability of thermographic examination and the normal thermographic image of the thoracolumbar region in the horse.Equine Vet J. 2004 May;36(4):306-12. doi: 10.2746/0425164044890652. Equine Vet J. 2004. PMID: 15163036
-
[Contemporary applications of infrared imaging in medical diagnostics].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2006;52(1):35-9; discussion 39-40. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2006. PMID: 17131845 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Infrared Thermography and Functional Parameters in the Lower Limbs of Hemiplegic Patients.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;15(4):542. doi: 10.3390/life15040542. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283098 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

