Heterogeneous subpopulations of GABAAR-responding neurons coexist across neuronal network scales and developmental stages in health and disease
- PMID: 38544574
- PMCID: PMC10966311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109438
Heterogeneous subpopulations of GABAAR-responding neurons coexist across neuronal network scales and developmental stages in health and disease
Abstract
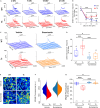
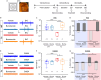
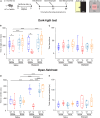
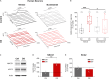
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in adults. Depolarizing GABA responses have been well characterized at neuronal-population average level during typical neurodevelopment and partially in brain disorders. However, no investigation has specifically assessed whether a mosaicism of cells with either depolarizing or hyperpolarizing/inhibitory GABAergic responses exists in animals in health/disease at diverse developmental stages, including adulthood. Here, we showed that such mosaicism is present in wild-type (WT) and down syndrome (DS) neuronal networks, as assessed at increasing scales of complexity (cultures, brain slices, behaving mice). Nevertheless, WT mice presented a much lower percentage of cells with depolarizing GABA than DS mice. Restoring the mosaicism of hyperpolarizing and depolarizing GABA-responding neurons to WT levels rescued anxiety behavior in DS mice. Moreover, we found heterogeneous GABAergic responses in developed control and trisomic human induced-pluripotent-stem-cells-derived neurons. Thus, a heterogeneous subpopulation of GABA-responding cells exists in physiological/pathological conditions in mouse and human neurons, possibly contributing to disease-associated behaviors.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Cellular neuroscience; Developmental neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L.C. is the cofounder and a scientific advisor at IAMA Therapeutics. L.C. and A.C. are inventors on the following patents: US 9,822,368 (granted 2017); EP 3083959 (granted 2019); JP 6490077 (granted 2019), US 11427836 (granted 2022), US 17/861676, EP 18717045.1, HK 62020014163.3, CA 3059389, CN 201880038547.7, JP 2020-505522, and IL 269952.
Figures




References
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi K., Yamada J., Takayama C., Oohira A., Fukuda A. NKCC1 activity modulates formation of functional inhibitory synapses in cultured neocortical neurons. Synapse. 2007;61:138–149. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

