A GMR enzymatic assay for quantifying nuclease and peptidase activity
- PMID: 38544982
- PMCID: PMC10966768
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1363186
A GMR enzymatic assay for quantifying nuclease and peptidase activity
Abstract
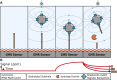
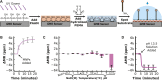
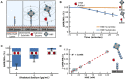
Hydrolytic enzymes play crucial roles in cellular processes, and dysregulation of their activities is implicated in various physiological and pathological conditions. These enzymes cleave substrates such as peptide bonds, phosphodiester bonds, glycosidic bonds, and other esters. Detecting aberrant hydrolase activity is vital for understanding disease mechanisms and developing targeted therapeutic interventions. This study introduces a novel approach to measuring hydrolase activity using giant magnetoresistive (GMR) spin valve sensors. These sensors change resistance in response to magnetic fields, and here, they are functionalized with specific substrates for hydrolases conjugated to magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). When a hydrolase cleaves its substrate, the tethered magnetic nanoparticle detaches, causing a measurable shift in the sensor's resistance. This design translates hydrolase activity into a real-time, activity-dependent signal. The assay is simple, rapid, and requires no washing steps, making it ideal for point-of-care settings. Unlike fluorescent methods, it avoids issues like autofluorescence and photobleaching, broadening its applicability to diverse biofluids. Furthermore, the sensor array contains 80 individually addressable sensors, allowing for the simultaneous measurement of multiple hydrolases in a single reaction. The versatility of this method is demonstrated with substrates for nucleases, Bcu I and DNase I, and the peptidase, human neutrophil elastase. To demonstrate a clinical application, we show that neutrophil elastase in sputum from cystic fibrosis patients hydrolyze the peptide-GMR substrate, and the cleavage rate strongly correlates with a traditional fluorogenic substrate. This innovative assay addresses challenges associated with traditional enzyme measurement techniques, providing a promising tool for real-time quantification of hydrolase activities in diverse biological contexts.
Keywords: DNA substrate; GMR; disease monitoring; enzymatic activity; giant magnetoresistive sensor; peptide substrate; point-of-care testing.
Copyright © 2024 Sveiven, Serrano, Rosenberg, Conrad, Hall and O’Donoghue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Antarnusa G., Esmawan A., Dwi Jayanti P., Rizki Fitriani S., Suherman A., Kinarya Palupi E., et al. (2022). Synthesis of Fe3O4 at different reaction temperatures and investigation of its magnetic properties on giant magnetoresistance (GMR) sensors for bio-detection applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 563, 169903. 10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169903 - DOI
-
- Bao Q., Lin D., Gao Y., Wu L., Fu J., Galaa K., et al. (2021). Ultrasensitive off-on-off fluorescent nanosensor for protamine and trypsin detection based on inner-filter effect between N,S-CDs and gold nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 168, 106409. 10.1016/j.microc.2021.106409 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

