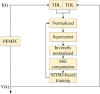
PEMFC model identification using a squeezenet developed by modified transient search optimization algorithm
- PMID: 38545225
- PMCID: PMC10965477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27555
PEMFC model identification using a squeezenet developed by modified transient search optimization algorithm
Abstract
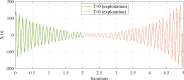
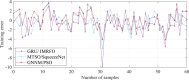
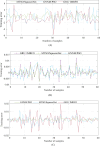
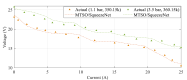
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) are promising sources of clean and renewable energy, but their performance and efficiency depend on an accurate modeling and identification of their system parameters. However, existing methods for PEMFC modeling suffer from drawbacks, such as slow convergence, high computational cost, and low accuracy. To address these challenges, this research work proposes an enhanced approach that combines a modified version of the SqueezeNet model, a deep learning architecture that reduces the number of parameters and computations, and a new optimization algorithm called the Modified Transient Search Optimization (MTSO) Algorithm, which improves the exploration and exploitation abilities of the search process. The proposed approach is applied to model the output voltage of the PEMFC under different operating conditions, and the results are compared with empirical data and two other state-of-the-art methods: Gated Recurrent Unit and Improved Manta Ray Foraging Optimization (GRU/IMRFO) and Grey Neural Network Model integrated with Particle Swarm Optimization (GNNM/PSO). The comparison shows that the proposed approach achieves the lowest Sum of Squared Errors (SSE) and the highest accuracy, demonstrating its superiority and effectiveness in PEMFC modeling. The proposed approach can facilitate the optimal design, control, and monitoring of PEMFC systems in various applications.
Keywords: Model identification; Modified transient search optimization algorithm; Output voltage; Proton exchange membrane fuel cells; Squeezenet; Sum of squared error.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Yuan Z., et al. Probabilistic decomposition‐based security constrained transmission expansion planning incorporating distributed series reactor. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020;14(17):3478–3487.
-
- Bo G., et al. Optimum structure of a combined wind/photovoltaic/fuel cell-based on amended Dragon Fly optimization algorithm: a case study. Energy Sources, Part A Recovery, Util. Environ. Eff. 2022;44(3):7109–7131.
-
- Yu D., et al. Energy management of wind-PV-storage-grid based large electricity consumer using robust optimization technique. J. Energy Storage. 2020;27
-
- Rajinikanth V., Razmjooy N., Ghadimi N. Frontiers of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging. IOP Publishing; 2022. Design of a system for melanoma diagnosis using image processing and hybrid optimization techniques.
-
- Jiang W., et al. Optimal economic scheduling of microgrids considering renewable energy sources based on energy hub model using demand response and improved water wave optimization algorithm. J. Energy Storage. 2022;55
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

