Evaluating the effect of a training program on type 2 diabetic patient's self-care: A quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 38545306
- PMCID: PMC10968271
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_353_23
Evaluating the effect of a training program on type 2 diabetic patient's self-care: A quasi-experimental study
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is one of the growing medical problems that affect people of all ages worldwide. Education is an important part of treatment in this chronic condition. The primary objectives of diabetes education include improving knowledge and skills, changing the patient's behavior, motivating them to follow therapeutic recommendations, establishing self-care habits, and increasing their psychological resilience. The authors aimed to examine the effect of a training program on type 2 diabetic patients' self care and investigate their perspectives on the educational program.
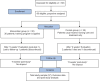
Materials and methods: The current study used a quasi-experimental, pretest-posttest design that was conducted in Iraq. Sixty patients who met the selection criteria were included in the study. Data were collected by demographic questionnaire and the Diabetes Self-Care Scale (DSCS). Data analysis was done by independent T-tests and Paired t-tests were used to compare the scores before and after the intervention.
Results: The sample included 60 diabetic patients with more than half of them being female (55%). Most respondents aged between 50 and 60 years old, and next to half of them had only primary school education. We found that training programs can improve self-care behavior among diabetic patients so that following the intervention, the self-care score increased from 1.79 ± 0.360 to 3.17 ± 0.546 (P = 0.01).
Conclusion: Since diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the whole individual's life, self-care plays an important role in preventing potential complications and improving quality of life. Training programs, on the other hand, increase the awareness and knowledge of patients and enable them to handle this chronic condition properly.
Keywords: Lifestyle modification; physical activity; self-care; training program; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
-
Behavioural interventions for type 2 diabetes: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(21):1-45. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074526 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of educational program based on the precede-proceed model on improving self-care behaviors in a semi-urban population with type 2 diabetes referred to health centers of Bavi, Iran.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017 Dec;11 Suppl 2:S759-S765. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017. PMID: 28669595
-
The role of education in type 2 diabetes treatment.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019 May;151:237-246. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 May 4. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31063855 Review.
References
-
- Raziani Y, Qadir SH, Hermis AH, Nazari A, Othman BS, Raziani S. Pistacia atlantica as an effective remedy for diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Aust J Herb Naturop Med. 2022;34:118–24.
-
- International Diabetes Federation (2021) 10th. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; Jan 10, 2022. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2021 and projections for 2045. Erişim tarihi.
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinal. 2018;14:88–98. - PubMed
-
- American Association of Diabetes Educators AADE7 self-care behaviors. Diabetes Educ. 2008;34:445–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous