The tyrosine kinase inhibitor Gefitinib reduces C. elegans stress-induced sleep, but not likely via LET-23/EGFR inhibition
- PMID: 38545437
- PMCID: PMC10966387
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001138
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor Gefitinib reduces C. elegans stress-induced sleep, but not likely via LET-23/EGFR inhibition
Abstract
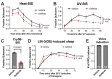
The anticancer drug Gefitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor with selectivity for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR/ErbB1). As the C. elegans EGF receptor LET-23 shares notable structural homology over its kinase domain with human EGFR, we wished to examine whether Gefitinib treatment can interfere with LET-23-dependent processes. We show that Gefitinib disrupts C. elegans stress-induced sleep (SIS) but does not impact EGF overexpression-induced sleep nor vulva induction. These findings indicate that Gefitinib does not interfere with LET-23 signaling and impairs SIS through an off-target mechanism.
Copyright: © 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest present.
Figures
References
-
- Barker AJ, Gibson KH, Grundy W, Godfrey AA, Barlow JJ, Healy MP, Woodburn JR, Ashton SE, Curry BJ, Scarlett L, Henthorn L, Richards L. Studies leading to the identification of ZD1839 (IRESSA): an orally active, selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeted to the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Jul 23;11(14):1911–1914. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(01)00344-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
