Diagnostic Performance of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among HCV High-Risk Patients
- PMID: 38546087
- PMCID: PMC11152387
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.3.1045
Diagnostic Performance of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among HCV High-Risk Patients
Abstract
Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is often diagnosed at advanced stage where hopeless for effective therapies. Identification of more reliable biomarkers for early detection of HCC is urgently needed. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) represent a unique liquid biopsy carrying comprehensive biological information of the primary tumor. Herein, we sought to develop a novel score based on the combination of the most significant CTCs biomarkers with routine laboratory tests for accurate detection of HCC.
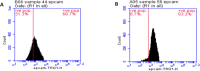
Material & methods: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), α-fetoprotein, albumin, and platelets count were assayed in HCC patients (98), liver cirrhosis patients (77). Areas under receiving operating curve (AUCs) were calculated and used for construction on novel score.
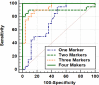
Results: A novel score named EpCAM-HCC = AFP (U/L) × 0.11 - Albumin (g/dl) × 1.5 + EpCAM % × 2.9 - Platelets count (×109)/L× 0.75 - 93. EpCAM-HCC score produce AUC of 1 for differentiate patients with HCC from those with liver cirrhosis with sensitivity and specificity of a cut-off 1.7 (i.e., less than 1.7 the case is considered cirrhotic, whereas above 1.7 it is considered HCC.
Conclusion: EpCAM-HCC score could replace AFP during screening of HCV patients and early detection of HCC.
Keywords: CTCs; EpCAM; HCV; Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Performance of Circulating Tumor Cells for Predicting of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis C Virus-High Risk Patients: Role of Liquid Biopsy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Jul 1;23(7):2541-2549. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.7.2541. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 35901363 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of Cytokeratins for Accurate Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Hepatitis C Virus High-Risk Patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Apr 1;25(4):1325-1332. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.4.1325. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38679993 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel score based on Angiogenic panel for accurate diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma among hepatitis C virus high-risk patients.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Nov;85:104572. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104572. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32987190
-
Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) and AFP-L3 Is Most Useful in Detection of Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients after Tumor Ablation and with Low AFP Level.Viruses. 2022 Apr 8;14(4):775. doi: 10.3390/v14040775. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological roles and clinical applications of EpCAM in HCC.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 14;16(1):319. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02095-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40087210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-17A and Interleukin-17F Gene Polymorphisms in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Jan 1;26(1):153-159. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.1.153. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 39873997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rashed WM, Kandeil MAM, Mahmoud MO, Ezzat S. Hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc) in egypt: A comprehensive overview. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2020;32(1):5. - PubMed
-
- Chen LT, Martinelli E, Cheng AL, Pentheroudakis G, Qin S, Bhattacharyya GS, et al. Pan-asian adapted esmo clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with intermediate and advanced/relapsed hepatocellular carcinoma: A tos-esmo initiative endorsed by csco, ismpo, jsmo, ksmo, mos and sso. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(3):334–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

