Exploring the therapeutic potential of DV-B-120 as an inhibitor of dengue virus infection
- PMID: 38546211
- PMCID: PMC11019862
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01258-23
Exploring the therapeutic potential of DV-B-120 as an inhibitor of dengue virus infection
Abstract
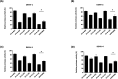
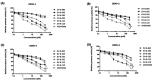
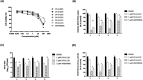
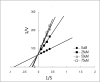
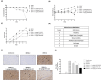
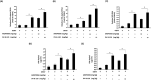
Dengue fever, an infectious disease prevalent in subtropical and tropical regions, currently lacks effective small-molecule drugs as treatment. In this study, we used a fluorescence peptide cleavage assay to screen seven compounds to assess their inhibition of the dengue virus (DENV) NS2B-NS3 protease. DV-B-120 demonstrated superior inhibition of NS2B-NS3 protease activity and lower toxicity compared to ARDP0006. The selectivity index of DV-B-120 was higher than that of ARDP0006. In vivo assessments of the antiviral efficacy of DV-B-120 against DENV replication demonstrated delayed mortality of suckling mice treated with the compound, with 60-80% protection against life-threatening effects, compared to the outcomes of DENV-infected mice treated with saline. The lower clinical scores of DENV-infected mice treated with DV-B-120 indicated a reduction in acute-progressive illness symptoms, underscoring the potential therapeutic impact of DV-B-120. Investigations of DV-B-120's ability to restore the antiviral type I IFN response in the brain tissue of DENV-infected ICR suckling mice demonstrated its capacity to stimulate IFN and antiviral IFN-stimulated gene expression. DV-B-120 not only significantly delayed DENV-2-induced mortality and illness symptoms but also reduced viral numbers in the brain, ultimately restoring the innate antiviral response. These findings strongly suggest that DV-B-120 holds promise as a therapeutic agent against DENV infection and highlight its potential contribution in addressing the current lack of effective treatments for this infectious disease.IMPORTANCEThe prevalence of dengue virus (DENV) infection in tropical and subtropical regions is escalating due to factors like climate change and mosquito vector expansion. With over 300 million annual infections and potentially fatal outcomes, the urgent need for effective treatments is evident. While the approved Dengvaxia vaccine has variable efficacy, there are currently no antiviral drugs for DENV. This study explores seven compounds targeting the NS2B-NS3 protease, a crucial protein in DENV replication. These compounds exhibit inhibitory effects on DENV-2 NS2B-NS3, holding promise for disrupting viral replication and preventing severe manifestations. However, further research, including animal testing, is imperative to assess therapeutic efficacy and potential toxicity. Developing safe and potent treatments for DENV infection is critical in addressing the rising global health threat posed by this virus.
Keywords: DV-B-120; NS2B-NS3 protease; competitive inhibitor; selectivity index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eltrombopag, an FDA-approved drug, inhibits dengue virus type 2 by targeting NS2B-NS3 protease.Virol Sin. 2025 Jun;40(3):439-450. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2025.05.009. Epub 2025 May 28. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40447137 Free PMC article.
-
Orthoflaviviral Inhibitors in Clinical Trials, Preclinical In Vivo Efficacy Targeting NS2B-NS3 and Cellular Antiviral Activity via Competitive Protease Inhibition.Molecules. 2024 Aug 27;29(17):4047. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174047. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Policresulen, a novel NS2B/NS3 protease inhibitor, effectively inhibits the replication of DENV2 virus in BHK-21 cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Sep;36(9):1126-36. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.56. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26279156 Free PMC article.
-
In silico evaluation of inhibitory potential of triterpenoids from Azadirachta indica against therapeutic target of dengue virus, NS2B-NS3 protease.J Vector Borne Dis. 2016 Apr-Jun;53(2):156-61. J Vector Borne Dis. 2016. PMID: 27353586
-
Recent advances in natural products as potential inhibitors of dengue virus with a special emphasis on NS2b/NS3 protease.Phytochemistry. 2022 Oct;202:113362. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113362. Epub 2022 Aug 7. Phytochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35948138 Review.
Cited by
-
Dengue and Flavivirus Co-Infections: Challenges in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Disease Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 10;26(14):6609. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146609. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li H-H, Su MP, Wu S-C, Tsou H-H, Chang M-C, Cheng Y-C, Tsai K-N, Wang H-W, Chen G-H, Tang C-K, Chung P-J, Tsai W-T, Huang L-R, Yueh YA, Chen H-W, Pan C-Y, Akbari OS, Chang H-H, Yu G-Y, Marshall JM, Chen C-H. 2023. Mechanical transmission of dengue virus by Aedes aegypti may influence disease transmission dynamics during outbreaks. EBioMedicine 94:104723. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104723 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

