Metabolite transport across central nervous system barriers
- PMID: 38546534
- PMCID: PMC11179608
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X241241908
Metabolite transport across central nervous system barriers
Abstract
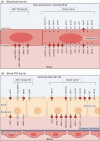
Metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is used to improve diagnostics and pathophysiological understanding of neurological diseases. Alterations in CSF metabolite levels can partly be attributed to changes in brain metabolism, but relevant transport processes influencing CSF metabolite concentrations should be considered. The entry of molecules including metabolites into the central nervous system (CNS), is tightly controlled by the blood-brain, blood-CSF, and blood-spinal cord barriers, where aquaporins and membrane-bound carrier proteins regulate influx and efflux via passive and active transport processes. This report therefore provides reference for future CSF metabolomic work, by providing a detailed summary of the current knowledge on the location and function of the involved transporters and routing of metabolites from blood to CSF and from CSF to blood.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; blood-CSF barrier; brain metabolism; metabolomics; transport mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Trezzi J-P, Galozzi S, Jaeger C, et al.. Distinct metabolomic signature in cerebrospinal fluid in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2017; 32: 1401–1408. - PubMed
-
- van Laarhoven A, Dian S, Aguirre-Gamboa R, et al.. Cerebral tryptophan metabolism and outcome of tuberculous meningitis: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18: 526–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

