Research progress of the netrins and their receptors in cancer
- PMID: 38546656
- PMCID: PMC10977403
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18241
Research progress of the netrins and their receptors in cancer
Abstract
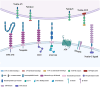
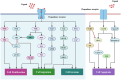
Netrins, a family of secreted and membrane-associated proteins, can regulate axonal guidance, morphogenesis, angiogenesis, cell migration, cell survival, and tumorigenesis. Four secreted netrins (netrin 1, 3, 4 and 5) and two glycosylphosphatidylinositols-anchored membrane proteins, netrin-G1 and G2, have been identified in mammals. Netrins and their receptors can serve as a biomarker and molecular therapeutic target for pathological differentiation, diagnosis and prognosis of malignant cancers. We review here the potential roles of the netrins family and their receptors in cancer.
Keywords: cancer; membrane; netrins; receptor; secreted.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The netrin protein family.Genome Biol. 2009;10(9):239. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-9-239. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Genome Biol. 2009. PMID: 19785719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Netrins and their receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;621:17-31. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-76715-4_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18269208 Review.
-
Netrin-G1: a novel glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-linked mammalian netrin that is functionally divergent from classical netrins.J Neurosci. 2000 Sep 1;20(17):6540-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-17-06540.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10964959 Free PMC article.
-
[Roles and mechanisms of netrins in cancer development].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018 Jun 25;34(6):876-887. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170495. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 29943533 Review. Chinese.
-
Netrins and their roles in placental angiogenesis.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:901941. doi: 10.1155/2014/901941. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25143950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Netrin-1 promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis and innervation through NEO1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 26:2025.07.22.666009. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.22.666009. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40777309 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The Role of Macrophage-Derived Netrin-1 in Inflammatory Diseases.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 23;15(7):921. doi: 10.3390/biom15070921. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Netrin-1 and B-cell maturation antigen expression in a large cohort of 361 lymphomas: sensitive and specific staining in plasmablastic lymphomas, and therapeutic perspectives.J Pathol Clin Res. 2025 May;11(3):e70027. doi: 10.1002/2056-4538.70027. J Pathol Clin Res. 2025. PMID: 40235169 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023-7/Youth Program of Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital
- Advanced Innovation Teams and Xinghu Scholars Program of Guangxi Medical University
- Guangxi Medical University Outstanding Young Talents Training Program
- 82060427/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82103297/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Guangxi Scholarship Fund of Guangxi Education Department
- 2021007/Nanning Qingxiu District Science and Technology Project
- 2021010/Nanning Qingxiu District Science and Technology Project
- 2021012/Nanning Qingxiu District Science and Technology Project
- Guangxi Medical and health key discipline construction project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

