The value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting severity of coronary involvement and long-term outcome of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38546902
- PMCID: PMC10978563
- DOI: 10.1186/s43044-024-00469-3
The value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting severity of coronary involvement and long-term outcome of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The value of counting inflammatory cells and especially their counting ratio in predicting adverse clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing revascularization has been shown, but the results of studies have been very diverse and paradoxical. The aim of the current study was to systematically review the studies that investigated the role of increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in predicting long-term clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
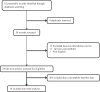
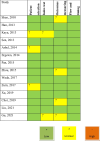
Methods: Data abstraction was independently performed by both un-blinded reviewers on deeply assessing Medline, Web of Knowledge, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and using the relevant keywords. The risk of bias for each study was assessed using the criteria outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and the QUADAS-2 tool. Statistical analysis was performed using the Stata software. Overall, 14 articles published between 2010 and 2021 were eligible for the final analysis.
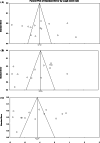
Results: A total of 20,846 ACS patients undergoing PCI were included. Higher values of NLR were associated with higher numbers of involved coronaries (RR: 1.175, 95%CI 1.021-1.353, P = 0.024). Increasing the value of NLR was associated with a 3.4 times increase in long-term death (RR: 3.424, 95%CI 2.325-5.025, P = 0.001). Similarly, higher values of NLR were significantly associated with a higher likelihood of long-term MACE (RR: 2.604, 95%CI 1.736-3.906, P = 0.001).
Conclusions: NLR has a high value in predicting both the severity of coronary artery involvement and long-term adverse clinical outcomes following the PCI procedure.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Major adverse cardiac event; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Percutaneous coronary intervention; Prognosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Demandt JPA, Zelis JM, Koks A, Smits GHJM, van der Harst P, Tonino PAL, Dekker LRC, van Het Veer M, Vlaar PJ. Prehospital risk assessment in patients suspected of non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12(4):e057305. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057305. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
