Clustering single-cell multi-omics data via graph regularized multi-view ensemble learning
- PMID: 38547401
- PMCID: PMC11015955
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae169
Clustering single-cell multi-omics data via graph regularized multi-view ensemble learning
Abstract
Motivation: Single-cell clustering plays a crucial role in distinguishing between cell types, facilitating the analysis of cell heterogeneity mechanisms. While many existing clustering methods rely solely on gene expression data obtained from single-cell RNA sequencing techniques to identify cell clusters, the information contained in mono-omic data is often limited, leading to suboptimal clustering performance. The emergence of single-cell multi-omics sequencing technologies enables the integration of multiple omics data for identifying cell clusters, but how to integrate different omics data effectively remains challenging. In addition, designing a clustering method that performs well across various types of multi-omics data poses a persistent challenge due to the data's inherent characteristics.
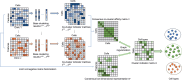
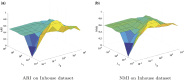
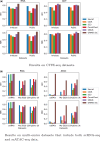
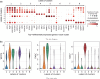
Results: In this paper, we propose a graph-regularized multi-view ensemble clustering (GRMEC-SC) model for single-cell clustering. Our proposed approach can adaptively integrate multiple omics data and leverage insights from multiple base clustering results. We extensively evaluate our method on five multi-omics datasets through a series of rigorous experiments. The results of these experiments demonstrate that our GRMEC-SC model achieves competitive performance across diverse multi-omics datasets with varying characteristics.
Availability and implementation: Implementation of GRMEC-SC, along with examples, can be found on the GitHub repository: https://github.com/polarisChen/GRMEC-SC.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
scMIC: A Deep Multi-Level Information Fusion Framework for Clustering Single-Cell Multi-Omics Data.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023 Dec;27(12):6121-6132. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2023.3317272. Epub 2023 Dec 5. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023. PMID: 37725723
-
Cancer subtype identification by multi-omics clustering based on interpretable feature and latent subspace learning.Methods. 2024 Nov;231:144-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.09.014. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Methods. 2024. PMID: 39326482
-
Autoencoder-assisted latent representation learning for survival prediction and multi-view clustering on multi-omics cancer subtyping.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Nov 27;20(12):21098-21119. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023933. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 38124589
-
Multi-omic and multi-view clustering algorithms: review and cancer benchmark.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 16;46(20):10546-10562. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky889. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30295871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal deep learning approaches for single-cell multi-omics data integration.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Sep 20;24(5):bbad313. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad313. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37651607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling spatial domains from spatial multi-omics data using dual-graph regularized ensemble learning.Commun Biol. 2025 Jun 20;8(1):945. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08372-6. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40542177 Free PMC article.
-
Recover then aggregate: unified cross-modal deep clustering with global structural information for single-cell data.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae485. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae485. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39356327 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics integration for both single-cell and spatially resolved data based on dual-path graph attention auto-encoder.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae450. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae450. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39293805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman NS. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am Stat 1992;46:175–85.
-
- Bellman R. Dynamic programming. Science 1966;153:34–7. - PubMed
-
- Brawand D, Soumillon M, Necsulea A. et al. The evolution of gene expression levels in mammalian organs. Nature 2011;478:343–8. - PubMed

