Systematic Optimization of Automated Phosphopeptide Enrichment for High-Sensitivity Phosphoproteomics
- PMID: 38548019
- PMCID: PMC11087715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100754
Systematic Optimization of Automated Phosphopeptide Enrichment for High-Sensitivity Phosphoproteomics
Abstract
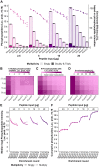
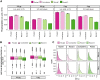
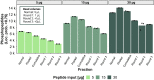
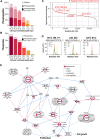
Improving coverage, robustness, and sensitivity is crucial for routine phosphoproteomics analysis by single-shot liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) from minimal peptide inputs. Here, we systematically optimized key experimental parameters for automated on-bead phosphoproteomics sample preparation with a focus on low-input samples. Assessing the number of identified phosphopeptides, enrichment efficiency, site localization scores, and relative enrichment of multiply-phosphorylated peptides pinpointed critical variables influencing the resulting phosphoproteome. Optimizing glycolic acid concentration in the loading buffer, percentage of ammonium hydroxide in the elution buffer, peptide-to-beads ratio, binding time, sample, and loading buffer volumes allowed us to confidently identify >16,000 phosphopeptides in half-an-hour LC-MS/MS on an Orbitrap Exploris 480 using 30 μg of peptides as starting material. Furthermore, we evaluated how sequential enrichment can boost phosphoproteome coverage and showed that pooling fractions into a single LC-MS/MS analysis increased the depth. We also present an alternative phosphopeptide enrichment strategy based on stepwise addition of beads thereby boosting phosphoproteome coverage by 20%. Finally, we applied our optimized strategy to evaluate phosphoproteome depth with the Orbitrap Astral MS using a cell dilution series and were able to identify >32,000 phosphopeptides from 0.5 million HeLa cells in half-an-hour LC-MS/MS using narrow-window data-independent acquisition (nDIA).
Keywords: Orbitrap Astral; Orbitrap Exploris; automation; data independent acquisition; phosphoproteomics; sequential enrichment.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Humphrey S.J., Karayel O., James D.E., Mann M. High-throughput and high-sensitivity phosphoproteomics with the EasyPhos platform. Nat. Protoc. 2018;13:1897–1916. - PubMed
-
- Lundby A., Andersen M.N., Steffensen A.B., Horn H., Kelstrup C.D., Francavilla C., et al. In vivo phosphoproteomics analysis reveals the cardiac targets of β-adrenergic receptor signaling. Sci. Signal. 2013;6 - PubMed
-
- Olsen J.V., Blagoev B., Gnad F., Macek B., Kumar C., Mortensen P., et al. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell. 2006;127:635–648. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

