A rapid inducible RNA decay system reveals fast mRNA decay in P-bodies
- PMID: 38548718
- PMCID: PMC10979015
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46943-z
A rapid inducible RNA decay system reveals fast mRNA decay in P-bodies
Abstract
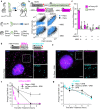
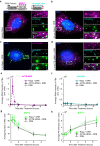
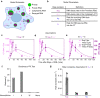
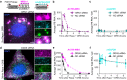
RNA decay is vital for regulating mRNA abundance and gene expression. Existing technologies lack the spatiotemporal precision or transcript specificity to capture the stochastic and transient decay process. We devise a general strategy to inducibly recruit protein factors to modulate target RNA metabolism. Specifically, we introduce a Rapid Inducible Decay of RNA (RIDR) technology to degrade target mRNAs within minutes. The fast and synchronous induction enables direct visualization of mRNA decay dynamics in cells. Applying RIDR to endogenous ACTB mRNA reveals rapid formation and dissolution of RNA granules in pre-existing P-bodies. Time-resolved RNA distribution measurements demonstrate rapid RNA decay inside P-bodies, which is further supported by knocking down P-body constituent proteins. Light and oxidative stress modulate P-body behavior, potentially reconciling the contradictory literature about P-body function. This study reveals compartmentalized RNA decay kinetics, establishing RIDR as a pivotal tool for exploring the spatiotemporal RNA metabolism in cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
A Rapid Inducible RNA Decay system reveals fast mRNA decay in P-bodies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 26:2023.04.26.538452. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.26.538452. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 28;15(1):2720. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46943-z. PMID: 37162943 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

