Lusca: FIJI (ImageJ) based tool for automated morphological analysis of cellular and subcellular structures
- PMID: 38548809
- PMCID: PMC10978859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57650-6
Lusca: FIJI (ImageJ) based tool for automated morphological analysis of cellular and subcellular structures
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Lusca: FIJI (ImageJ) based tool for automated morphological analysis of cellular and subcellular structures.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 19;14(1):9026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59795-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38641697 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
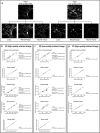
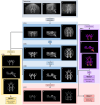
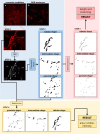
The human body consists of diverse subcellular, cellular and supracellular structures. Neurons possess varying-sized projections that interact with different cellular structures leading to the development of highly complex morphologies. Aiming to enhance image analysis of complex biological forms including neurons using available FIJI (ImageJ) plugins, Lusca, an advanced open-source tool, was developed. Lusca utilizes machine learning for image segmentation with intensity and size thresholds. It performs particle analysis to ascertain parameters such as area/volume, quantity, and intensity, in addition to skeletonization for determining length, branching, and width. Moreover, in conjunction with colocalization measurements, it provides an extensive set of 29 morphometric parameters for both 2D and 3D analysis. This is a significant enhancement compared to other scripts that offer only 5-15 parameters. Consequently, it ensures quicker and more precise quantification by effectively eliminating noise and discerning subtle details. With three times larger execution speed, fewer false positive and negative results, and the capacity to measure various parameters, Lusca surpasses other existing open-source solutions. Its implementation of machine learning-based segmentation facilitates versatile applications for different cell types and biological structures, including mitochondria, fibres, and vessels. Lusca's automated and precise measurement capability makes it an ideal choice for diverse biological image analyses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton. Int. 2004;11:36–42.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

