Protein-altering variants at copy number-variable regions influence diverse human phenotypes
- PMID: 38548989
- PMCID: PMC11018521
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01684-z
Protein-altering variants at copy number-variable regions influence diverse human phenotypes
Abstract
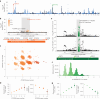
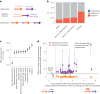
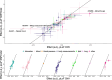
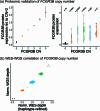
Copy number variants (CNVs) are among the largest genetic variants, yet CNVs have not been effectively ascertained in most genetic association studies. Here we ascertained protein-altering CNVs from UK Biobank whole-exome sequencing data (n = 468,570) using haplotype-informed methods capable of detecting subexonic CNVs and variation within segmental duplications. Incorporating CNVs into analyses of rare variants predicted to cause gene loss of function (LOF) identified 100 associations of predicted LOF variants with 41 quantitative traits. A low-frequency partial deletion of RGL3 exon 6 conferred one of the strongest protective effects of gene LOF on hypertension risk (odds ratio = 0.86 (0.82-0.90)). Protein-coding variation in rapidly evolving gene families within segmental duplications-previously invisible to most analysis methods-generated some of the human genome's largest contributions to variation in type 2 diabetes risk, chronotype and blood cell traits. These results illustrate the potential for new genetic insights from genomic variation that has escaped large-scale analysis to date.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Update of
-
Hidden protein-altering variants influence diverse human phenotypes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 9:2023.06.07.544066. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.07.544066. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Genet. 2024 Apr;56(4):569-578. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01684-z. PMID: 37333244 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- OT2 OD026556/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HG012698/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG013110/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025315/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023121/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025277/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026550/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006855/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026553/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023205/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026557/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026554/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023163/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023206/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023176/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026548/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023196/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL154537/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH124393/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026551/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026552/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026549/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL160061/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL150334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025337/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HG006855/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026555/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 ES030554/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025276/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

