Characterization of tumoricidal activities mediated by a novel immune cell regimen composing interferon-producing killer dendritic cells and tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 38549061
- PMCID: PMC10979599
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12101-3
Characterization of tumoricidal activities mediated by a novel immune cell regimen composing interferon-producing killer dendritic cells and tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
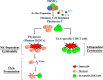
Background: Although immune cell therapy has long been used for treating solid cancer, its efficacy remains limited. Interferon (IFN)-producing killer dendritic cells (IKDCs) exhibit cytotoxicity and present antigens to relevant cells; thus, they can selectively induce tumor-associated antigen (TAA)-specific CD8 T cells and may be useful in cancer treatment. Various protocols have been used to amplify human IKDCs from peripheral sources, but the complexity of the process has prevented their widespread clinical application. Additionally, the induction of TAA-specific CD8 T cells through the adoptive transfer of IKDCs to immunocompromised patients with cancer may be insufficient. Therefore, we developed a method for generating an immune cell-based regimen, Phyduxon-T, comprising a human IKDC counterpart (Phyduxon) and expanded TAA-specific CD8 T cells.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from ovarian cancer patients were cultured with human interleukin (hIL)-15, hIL-12, and hIL-18 to generate Phyduxon-T. Then, its phenotype, cytotoxicity, and antigen-presenting function were evaluated through flow cytometry using specific monoclonal antibodies.
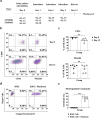
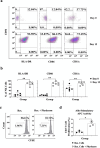
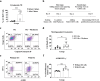
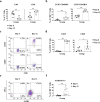
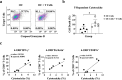
Results: Phyduxon exhibited the characteristics of both natural killer and dendritic cells. This regimen also exhibited cytotoxicity against primary ovarian cancer cells and presented TAAs, thereby inducing TAA-specific CD8 T cells, as evidenced by the expression of 4-1BB and IFN-γ. Notably, the Phyduxon-T manufacturing protocol effectively expanded IFN-γ-producing 4-1BB+ TAA-specific CD8 T cells from peripheral sources; these cells exhibited cytotoxic activities against ovarian cancer cells.
Conclusions: Phyduxon-T, which is a combination of natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and TAA-specific CD8 T cells, may enhance the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: 4-1BB; IKDCs; Immunotherapy; Phyduxon-T; TAA-specific CD8 T cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.-M. L., C.-H. F., and Y.-F. C. are employees of FullHope Biomedical Co.,Ltd. They also hold shares in FullHope Biomedical Co.,Ltd. J.-M. L., K.-L. L., C.-H. F., and Y.-F. C. are inventors of patent applications (Application No. 18/170,671). All authors declare no other conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro induction of tumor-specific human lymphocyte antigen class I-restricted CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes by ovarian tumor antigen-pulsed autologous dendritic cells from patients with advanced ovarian cancer.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Sep;183(3):601-9. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.107097. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10992180
-
Induction of ovarian tumor-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes by acid-eluted peptide-pulsed autologous dendritic cells.Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Sep;96(3):422-30. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(00)00916-9. Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10960637
-
Analysis and characterization of antitumor T-cell response after administration of dendritic cells loaded with allogeneic tumor lysate to metastatic melanoma patients.J Immunother. 2008 Jan;31(1):101-12. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e318159f5ba. J Immunother. 2008. PMID: 18157017 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinically feasible approaches to potentiating cancer cell-based immunotherapies.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(4):851-69. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1009814. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25933181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Licensing of killer dendritic cells in mouse and humans: functional similarities between IKDC and human blood γδ T-lymphocytes.J Immunotoxicol. 2012 Jul-Sep;9(3):259-66. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2012.685528. Epub 2012 May 27. J Immunotoxicol. 2012. PMID: 22632132 Review.
Cited by
-
TME-NET: an interpretable deep neural network for predicting pan-cancer immune checkpoint inhibitor responses.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae410. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae410. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39167797 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

