Efficacy of optimal nutraceutical combination in treating PCOS characteristics: an in-silico assessment
- PMID: 38549084
- PMCID: PMC10979615
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-024-01571-y
Efficacy of optimal nutraceutical combination in treating PCOS characteristics: an in-silico assessment
Abstract
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a serious health condition affecting women of reproductive age. High prevalence of PCOS and associated metabolic complications needs effective treatment and management. This study evaluated the efficacy of optimal nutraceutical combinations in improving PCOS characteristics using system biology-based mathematical modelling and simulation.
Methods: A shortlisting of eight potent nutraceuticals was carried out with literature search. Menstrual cycle model was used to perform simulations on an in-silico population of 2000 individuals to test individual and combined effects of shortlisted nutraceuticals on five PCOS characteristics [oligomenorrhea, anovulation, hirsutism, infertility, and polycystic ovarian morphology (PCOM)] for a duration of 6 months. Efficacy was tested across lean and obese phenotypes and age groups.
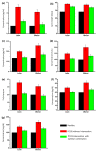
Results: Individual assessment of nutraceuticals revealed seven most potent compounds. Myo-inositol among them was observed to be the most effective in alleviating the PCOS characteristics. The in-silico population analysis showed that the combination of melatonin and ALA along with myo-inositol was efficacious in restoring the hormonal balance across age-groups and Body Mass Index (BMI) categories.
Conclusion: Supplementation with the combination of myo-inositol, melatonin, and ALA demonstrated potential in managing PCOS symptoms in our in-silico analysis of a heterogeneous population, including lean and obese phenotypes across various severities and age groups, over a 6-month period. Future clinical studies are recommended to validate these findings.
Keywords: In-silico; Intervention; Nutraceutical; Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS); Systems-biology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Mihanfar A, Nouri M, Roshangar L, Khadem-Ansari MH, Polyphenols. Natural compounds with promising potential in treating polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Biol. 2021;21(2). 10.1016/j.repbio.2021.100500. - PubMed
-
- Mahran A. The relationship between Anti-müllerian hormone and the clinical, biochemical and sonographic parameters in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Middle East Fertil Soc J. 2016;21(1):11–5. doi: 10.1016/j.mefs.2015.06.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

