Long-term toxicities after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with or without total body irradiation: a population-based study in Korea
- PMID: 38549384
- PMCID: PMC10982063
- DOI: 10.3857/roj.2023.00871
Long-term toxicities after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with or without total body irradiation: a population-based study in Korea
Abstract
Purpose: To compare long-term toxicity incidences, including secondary cancer (SC) with or without total body irradiation (TBI), in Asian patients receiving allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) using a nationwide database.
Materials and methods: We identified 4,554 patients receiving HSCT for leukemic disease from 2009 to 2016 using the healthcare bigdata system of Korea. Incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for SC, cataracts, hypothyroidism, chronic kidney disease (CKD), myocardial infarction, or strokes were compared, and standardized incidence ratios (SIR) of SC was also estimated.
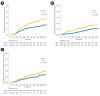
Results: TBI was conducted on 1,409 patients (30.9%). No overall survival differences based on TBI were observed. With a median follow-up duration of 58.2 months, 143 patients were diagnosed with subsequent SC (3.4%). Incidence rates per 1,000 person-year were 6.56 (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.8-8.8) and 7.23 (95% CI, 5.9-8.8) in the TBI and no-TBI groups, respectively (p = 0.594). Also, the SIR (95% CI) was not significantly increased by TBI (1.32 [0.86-1.94] vs. 1.39 [1.08-1.77] in the no-TBI group). In the young age group (0-19 years), SIRs were increased in both groups regardless of TBI (8.60 vs. 11.96). The IRRs of cataracts (1.60; 95% CI, 1.3-2.0), CKD (1.85; 95% CI, 1.3-2.6), and hypothyroidism (1.50; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1) were significantly increased after TBI. However, there were no significant differences in the occurrence of myocardial infarction and stroke according to TBI.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that modern TBI may not additionally increase the risk of SC after allogeneic HSCT, although increased risks of other diseases were noted. Physicians should carefully consider individualized risks and benefits of TBI, with a particular focus by age group.
Keywords: Cataract; Chronic renal insufficiency; Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation; Secondary malignancy; Total body irradiation; Whole-body irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic kidney dysfunction in patients alive without relapse 2 years after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009 Oct;15(10):1251-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.05.016. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19747632
-
Outcomes of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation with intensity-modulated total body irradiation by helical tomotherapy: a 2-year prospective follow-up study.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):2616-2625. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2125171. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 36254468 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of long-term mortality after total body irradiation-based and melphalan-based chemotherapy conditioning for acute myeloid leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2023 Aug;102(8):2199-2211. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05318-y. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37347269 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Total Body Irradiation-Based Myeloablative Conditioning Regimens in Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transplant Cell Ther. 2021 Jul;27(7):620.e1-620.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2021.03.026. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021. PMID: 33798768
-
Current Use of Total Body Irradiation in Haploidentical Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Mar 1;36(8):e55. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e55. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33650334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta T, Kannan S, Dantkale V, Laskar S. Cyclophosphamide plus total body irradiation compared with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide as a conditioning regimen prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2011;4:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Gooptu M, Kim HT, Ho VT, et al. A comparison of the myeloablative conditioning regimen fludarabine/busulfan with cyclophosphamide/total body irradiation, for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in the modern era: a cohort analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:1733–40. - PubMed
-
- Jeon YW, Yoon S, Min GJ, et al. Clinical outcomes of fludarabine and melphalan with an 800 cGy total body irradiation conditioning regimen in patients with refractory or relapsed aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019;19:345–55. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources