Short- and long-term effects of Covid-19 pandemic on health care system for individuals with eating disorders
- PMID: 38550538
- PMCID: PMC10973158
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1360529
Short- and long-term effects of Covid-19 pandemic on health care system for individuals with eating disorders
Abstract
Introduction: The Covid-19 pandemic and its consequences have negatively impacted the incidence of EDs, determining a substantial burden on patients, caregivers and healthcare systems world-wide. This literature review aims to investigate the short- and long-term effects of the pandemic on care provider systems, exploring the possibility of "rethinking" ED care programs.
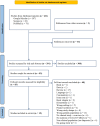
Methods: Records were systematically (following the PRISMA guidelines) identified through PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus searching.
Results: The Covid-19 pandemic led to an abrupt and substantial increase in pediatric and adolescent ED visits and hospital admissions. Despite a decline in the second-year post-onset, absolute visit volumes remained elevated relative to pre-pandemic levels. Barriers to access specialist ED care have emerged, including socio-economic status and a lack of public outpatient services. Consequently, this situation has prompted healthcare providers to explore innovative bridge plans and multidisciplinary telehealth solutions to face such challenges.
Discussion: Challenges in insurance shifts, treatment disruptions and discharge planning underscore the need for comprehensive strategies in ED care. Overall, our findings highlight the importance of adopting multidisciplinary approaches, implementing location-specific plans, and integrating telehealth to effectively address the evolving challenges posed by the pandemic and enhance the efficiency of ED specialist care programs.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; eating disorders; healthcare system; short-and long-term effects; systematic literature review.
Copyright © 2024 Boltri, Brusa, Apicella and Mendolicchio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing. (2013).
-
- Gilsbach S, Plana MT, Castro-Fornieles J, Gatta M, Karlsson GP, Flamarique I, et al. . Increase in admission rates and symptom severity of childhood and adolescent anorexia nervosa in Europe during the COVID-19 pandemic: data from specialized eating disorder units in different European countries. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2022) 16:46. doi: 10.1186/s13034-022-00482-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources