Potential anti-hyperglycemic activity of black tea theaflavins through inhibiting α-amylase
- PMID: 38550892
- PMCID: PMC10972827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101296
Potential anti-hyperglycemic activity of black tea theaflavins through inhibiting α-amylase
Abstract
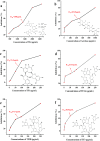
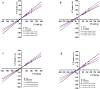
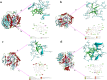
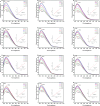
Hyperglycemia can cause early damage to human bady and develop into diabates that will severely threaten human healthy. The effectively clinical treatment of hyperglycemiais is by inhibiting the activity of α-amylase. Black tea has been reported to show inhibitory effect on α-amylase and can be used for hyperglycemia treatment. However, the mechanism underlying is unclear. In this study, in vivo experiment showed that black tea theaflavins extract (BTE) effectively alleviated hyperglycemia. In vitro experiment showed that the effects may be caused by the interation between theaflavins and α-amylase. While TF1 and TF3 were mixed type inhibitors of α-amylase, TF2A and TF2B were competitive inhibitors of α-amylase. Molecular docking analysis showed that theaflavins monomers interacted with the hydrophobic region of α-amylase. Further study verified that monomer-α-amylase complex was spontaneously formed depending on hydrophobic interactions. Taken together, theaflavins showed potential anti-hyperglycemia effect via inhibiting α-amylase activity. Our results suggested that theaflavins might be utilized as a new type of α-amylase inhibitor to prevent and cure hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Black tea; Hypoglycemic activity; Interaction mechanism; Theaflavins; α-amylase.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Abdollahi K., Ince C., Condict L., Hung A., Kasapis S. Combined spectroscopic and molecular docking study on the pH dependence of molecular interactions between β-lactoglobulin and ferulic acid. Food Hydrocolloids. 2020;101 doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105461. - DOI
-
- Abeywickrama K.R.W., Ratnasooriya W.D., Amarakoon A.M.T. Oral hypoglycaemic, antihyperglycaemic and antidiabetic activities of Sri Lankan broken Orange pekoe Fannings (BOPF) grade black tea (Camellia sinensis L.) in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2011;135(2):278–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.02.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashwar B.A., Gani A., Shah A., Wani I.A., Masoodi F.A. Preparation, health benefits and applications of resistant starch—A review. Starch-Stärke. 2016;68(3–4):287–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105094. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

